Write down the mathematical form of Ampere's circuital law.
Important Questions on Moving Charges and Magnetism
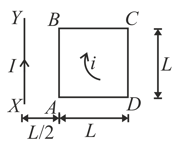
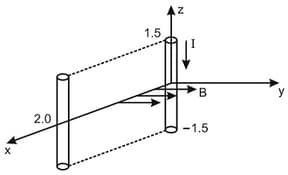
In a thin rectangular metallic strip a constant current I flows along the positive x - direction, as shown in the figure. The length, width and thickness of the strip are l, w and d, respectively. A uniform magnetic field is applied on the strip along positive y - direction. Due to this the charge carries experience a net deflection along the z-direction. This results in accumulation of charge carriers on the surface PQRS and appearance of equal opposite charges on the face opposite to PQRS. A potential difference along the z - direction is thus developed. Charge accumulation continues until the magnetic force is balanced by the electric force. The current is assumed to be uniformly distributed on the cross section of the strip and carried by electrons.
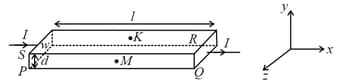
Consider two different metallic strips (1 and 2) of the same material. Their lengths are the same, widths are and and thicknesses are and , respectively. Two points and are symmetrically located on the opposite faces parallel to the - plane (see figure). and are the potential differences between and in strips 1 and 2 respectively. Then, for a given current flowing through them in a given magnetic field strength , the correct statement(s) is (are)
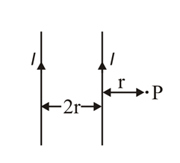
Two very long straight wires are set parallel to each other. Each carries a current in the same direction and the separation between them is The intensity of the magnetic field at point as shown in the figure is _________.
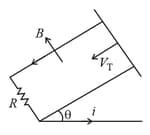
A copper rod of mass slides under gravity on two smooth parallel rails distance apart and set an angle to the horizontal. At the bottom, the rails are joined by a resistance in figure. There is a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the rails. The terminal velocity of rod is
A current is flowing along an infinite, straight wire, in the positive direction and the same current is flowing along a similar parallel wire apart, in the negative direction. A point is at a perpendicular distance from the first wire and from the second. What will be the magnitude of the magnetic field of ?
A very long straight wire of radius carries current . Intensity of magnetic field at a point lying at a perpendicular distance from the axis is _____ .
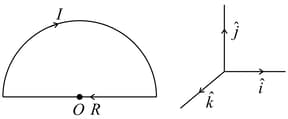
The magnitude and direction of a force vector acting on a unit length of thin wire carrying a current at point , if the wire has a semicircular shape of radius as shown in the figure.
In a thin rectangular metallic strip a constant current I flows along the positive x - direction, as shown in the figure. The length, width and thickness of the strip are l, w and d, respectively. A uniform magnetic field is applied on the strip along positive y - direction. Due to this the charge carries experience a net deflection along the z-direction. This results in accumulation of charge carriers on the surface PQRS and appearance of equal opposite charges on the face opposite to PQRS. A potential difference along the z - direction is thus developed. Charge accumulation continues until the magnetic force is balanced by the electric force. The current is assumed to be uniformly distributed on the cross section of the strip and carried by electrons.

Consider two different metallic strips (1 and 2) of same dimensions (length , width and thickness ) with carrier densities and , respectively. Strip 1 is placed in magnetic field and strip 2 is placed in magnetic field , both along positive -directions. Then and are the potential differences developed between and in strips 1 and 2 respectively. Assuming that the current is the same for both strips, the correct option(s) is (are)

