You push a block against a horizontal spring, compressing the spring by Then you release the block, and the spring sends it sliding across a tabletop. It stops from where you released it. The spring constant is . What is the block-table coefficient of kinetic friction?

Important Questions on Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
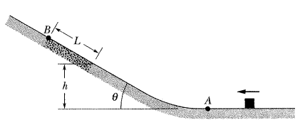
In the figure shown below a block slides along a path that is without friction until the block reaches the section of length which begins at height on a ramp of angle In that section, the coefficient of kinetic friction is . The block passes through point . If the block can reach point (where the friction ends), what is its speed there, and if it cannot, what is its greatest height above ?
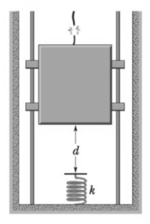
The cable of the Elevator cab in figure snaps when the cab is at rest at the first floor, where the cab bottom is a distance Above a spring of spring constant . A safety device clamps the cab against guide rails so that a constant frictional force of Opposes the cab's motion. (a) Find the speed of the cab just before it hits the spring. (b) Find the maximum distance that the spring is compressed (the frictional force still acts during this compression).
(c) Find the distance that the cab will bounce back up the shaft.
(d) Using conservation of energy, find the approximate total distance that the cab will move before coming to rest. (Assume that the frictional force on the cab is negligible when the cab is stationary.)
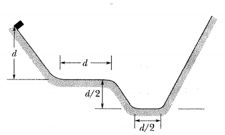
In the figure shown below block is released from rest at height and slides down a frictionless ramp and onto a first plateau, which has length and where the coefficient of kinetic friction is . If the block is still moving, it then slides down a second frictionless ramp through height and onto a lower plateau, which has length and where the coefficient of kinetic friction is again If the block is still moving, it then slides up a frictionless ramp until it (momentarily) stops. Where does the block stop? If its final stop is on a plateau, state which one and give the distance from the left edge of that plateau. If the block reaches the ramp, give the height above the lower plateau where it momentarily stops.