Proteins
Proteins: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Non Essential Amino Acid,Tertiary Structure of a Protein,Primary Structure of a Protein, etc.
Important Questions on Proteins
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: A protein is imagined as a line, the left end represented by first amino acid (C-terminal) and the right end represented by last amino acid (N-terminal).
Statement II: Adult human haemoglobin, consists of 4 subunits (two subunits of type and two subunits of type).
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which among the following is a non-polymeric biomolecule that can be found in acid insoluble fraction?
Assertion: Active site of an enzyme is a crevice or pocket into which the substrate fits.
Reason: In tertiary structure of protein chain when folds upon itself, the chain criss-crosses itself, and many crevices are formed.
The correct option among the following is:
Choose the correct statements from the following:
A) Protein threads exist throughout as rigid rods.
B) By dehydration, a glycosidic bond is formed.
C) Adult human haemoglobin has subunits.
D) Litmus paper does not turn into blue colour with iodine.
For being functional, a protein has to acquire at least
Amino acids have both an amino group and a carboxyl group in their structure. Which amongst the following is an amino acid?
A protein with isoelectric point was isolated. It was prepared in three different buffers and with and , respectively. With respect to the net charge on protein , the correct option is
Proteins in biological systems are polypeptides that are exclusively made from -amino acids. A peptide, , with -amino acids of a particular sequence always adopts a right-handed alpha helical structure. Under identical conditions, if all the amino acids of the peptide are changed to -amino acids, then the expected conformation from the options given below would be _____.
Three given polypeptides and , of same size and same , have a single aspartic acid in each of them. In polypeptide , the aspartic acid residue is on the surface. In polypeptide , it is surrounded by negatively charged residues, whereas in polypeptide it is deeply buried in a hydrophobic core. of the side chain carboxylate of free (in solution) aspartic acid is . The polypeptides are in a buffer of . The change in of the aspartic acid side chain carboxylate in the polypeptides and is likely to
A small viral peptide can insert its amino acids (represented as a barrel) into the lipid bilayer as depicted in the figure given below.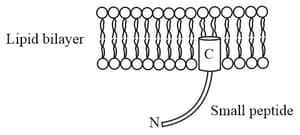
The table depicts the different properties of amino acids.
| Properties | |||
| Polar and uncharged | Polar and charged | Non-polar and hydrophobic | |
| Amino acids | Gly | Asp | Ala |
| Ser | Glu | Val | |
| Thr | Lys | Leu | |
| Cys | Arg | Ile | |
| Asn | His | Pro | |
| Gln | - | Met | |
| Tyr | - | Phe | |
| - | - | Trp | |
