Meiosis
Meiosis: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Meiosis, Homologous Chromosomes, Crossing Over, Significance of Meiosis, Chiasmata, Synaptonemal Complex, Pachytene, Leptotene, Bivalent, Zygotene, Diplotene, Interkinesis, Diakinesis and, Recombinase
Important Questions on Meiosis
Why are there haploid cells in meiosis compared to diploids in mitosis?
Why does meiosis form haploid cells only?
Name the stage of meiosis after which cytokinesis results in the formation of four daughter cells.
Arrange the following stages in the order they follow.
(i) Anaphase I
(ii) Telophase II
(iii) Prophase II
(iv) Cytokinesis
(v) Interkinesis
In the process of meiosis, which stage comes just after interkinesis?
In telophase II, spindle fibres contract and split the chromosome into sister chromatids that move to opposite poles.
Write the key differences between Telophase I and Telophase II?
Mark the image that represents the telophase II of meiosis?
Write the key difference between Prophase I and Prophase II.
In Prophase II, spindle fibres contract and split the chromosome into sister chromatids that move to opposite poles.
Which among the following image represents the prophase II of meiosis?
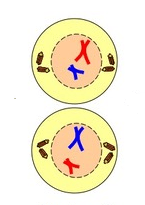
Identify and name the stage of meiosis II that has been shown in the image.
There are _____ numbers of cells produced at the end of the cytokinesis after meiosis from one cell. (Answer in numeric form)
The number of cells produced at the end of the cytokinesis after meiosis is two.
What is the number of cells produced at the end of the cytokinesis after meiosis? (Answer in numeric form)
How many cells are produced at the end of the cytokinesis after meiosis?
Define cytokinesis. What is the number of cells produced after the end of cytokinesis if a cell has undergone meiosis?
The reformation of the nucleus around each set of chromosome takes place in
