Gametogenesis
Gametogenesis: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Spermatogenesis, Oogenesis, Graafian follicle, Gametogenesis, Spermatozoa, Spermiogenesis, Zona Pellucida, Spermiation, Oogonia, Spermatids, Secondary Oocyte, Polar Body, Primary Oocytes and, Primary Spermatocytes
Important Questions on Gametogenesis
In which of the following phases all organisms have to pass through it before they can reproduce sexually?
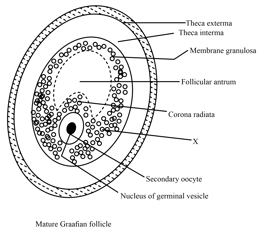
Choose the correct option to label the region .
A human ovum completes its second meiosis:
Read the statements carefully and select the incorrect one with respect to gonadotrophins:
Germ cells in human males and ova in females are:
How many polar bodies would be formed during the formation of 10 menstrual cycles, considering one secondary oocyte was formed in each cycle?
For normal fertility how many percentage of sperms must have normal shape and size ?
What is likely to happen to the polar bodies formed after each meiotic cycle in oogenesis? Give a reason to support your answer.
In an individual with low testosterone levels. if the semen sample of such an individual is collected, what is likely to be observed?
In an individual with low testosterone levels. Which process in spermatogenesis is likely to not happen?
Gametogenesis is the process of production of gametes. In males, it is spermatogenesis and in females it is oogenesis. The cells in the germline that undergo meiosis, primary spermatocytes or primary oocytes, are derived from the zygote by a long series of mitosis before the onset of the two meiotic cycles to form the mature gametes. Testosterone is an androgen that plays an important role in the formation and release of sperm from the seminiferous tubules. What is the count of chromosomes after the first and second meiotic divisions in the formation of sperms? Give a reason to support your answer.
Identify A, B and C.
Hypothalamus Anterior pituitary Leydig cells Spermatogenesis
Arrange the following parts of Graafian follicle from outside to inside in a sequence
(A) Secondary oocyte
(B) Corona radiata
(C) Zona pellucida
(D) Theca externa
(E) Membrana granulosa
(F) Theca interna
(G) Antrum
Where does secondary oocyte develop in human females?
'X' is a hormone which is secreted under the influence of GnRH. Identify 'X' and the correct marked structures (A - D) from the figure given below on which 'X' acts to stimulate secretion of some factors to help in spermiogenesis.
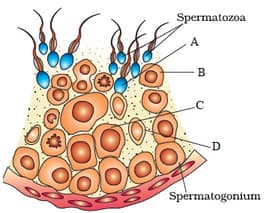
Complete the analogy:
FSH : Sertoli cells :: LH : ____.
