Leaf: Structure, Types and Modifications
Leaf: Structure, Types and Modifications: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as leaf venation, leaf, petiole, leaf base and lamina.
Important Questions on Leaf: Structure, Types and Modifications
In Opuntia, spines are modification of:
Explain opposite phyllotaxy.
Define leaf hook.
The leaf lamina is the expanded and green part of the leaf.
Which among the following part of the leaf provides a large surface area to carry out photosynthesis?
Mention the function of leaf lamina.
Define the lamina of leaf.
What term is given to the arrangement of leaves on the stem?
Fill in the blank with the correct option from the bracket.
Reticulate venation is found in most of the _____ plants. (monocot, bryophyte, dicot)
What is the difference in the venation (vein arrangement) of a peepal leaf and a grass leaf?
In which part of the plant are the veins found?
Fill the table below:

Observe the leaves of a mango tree, jack tree, bamboo, paddy, teak, and coconut tree and classify them into two based on venation.
Choose the odd one out.
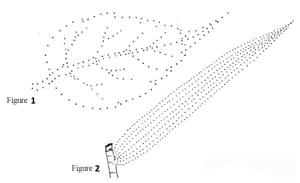
Notice the pattern of the leaves in the picture. What differences did you notice between the two leaves?
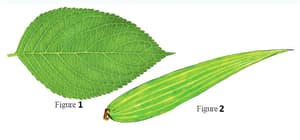
Notice the pattern of the leaves in the picture. Complete the picture by joining the dots, starting from the leaf stalk.
Give an example for leaf modified into tendrils.
Give an example for leaf modified into pitcher.
Give an example for leaf modified into spines.
Wild pea and glory lily are examples of _____(leaf tendrils/leaf spines).
