Octet rule and its limitations
Octet rule and its limitations: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Atom, Chemical Bonds, Covalent Bond, Valence Electrons, Lewis Dot Structure, Formal Charge, Types of Chemical Bonds, Double Covalent Bond, Triple Covalent Bond, Single Covalent Bond and, Expanded Octet
Important Questions on Octet rule and its limitations
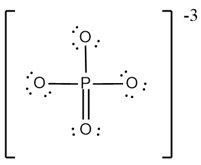
What are the formal charges on and in the Lewis (electron dot) structure of the phosphate oxyanion represented in the figure?
Identify odd-electron molecules from the following:
Which of the following oxides is an odd-electron molecule.
Which of the following noble gas compound has hybridisation?
If an element is represented by its Lewis symbols as 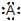 , then A may be
, then A may be
What will be the probable chemical formula if the valence shell of element contain three electrons, while the valence shell of element contain six electrons are combined?
In the Lewis structure, the formal charge on the central atom of is
Maximum number of lone pairs is present in Lewis dot structure of which compound?
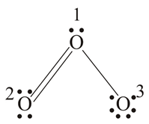
In ion formal charge on the oxygen atom of bond is
In which of the following molecule central atom is having complete octet?
Which of the following is not an application of formal charge?
Lewis symbols are used to depict _____ in simple molecules.
The number of dots around the symbol represents the number of _____ electrons.
In molecule, the number of bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons are:
Which of the following is a Super octet molecule?
Metals lose electrons during ionization. This change is called
Assertion. The atoms in a covalent molecule are said to share electrons, yet some covalent molecules are polar.
Reason. In a polar covalent molecule, the shared electrons spend more time than average near one of the atoms
Assertion. When two hydrogen atoms approach each other to form a covalent bond, nearly of energy is released.
Reason. When two atoms approach each other to form a covalent bond between them, potential energy of the system continuously decreases.
Assertion. is not a stable molecule.
Reason. A stable molecule must have 8 electrons around the central atom, i.e., octet rule should be satisfied.
