Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Carbohydrates, Glucose, Biomolecules, Biochemistry, Cellulose, Glycogen, Starch, Classification of Carbohydrates, Sucrose, Fructose, Lactose, Monosaccharides, Structure of Sucrose, Maltose and, Oligosaccharides
Important Questions on Carbohydrates
The products obtained on hydrolysis of sucrose are:
The simplest carbohydrates which cannot be hydrolysed to smaller molecules are known as
Which of the following carbohydrate is a reducing sugar?
Which of the following reactions and facts of D-glucose cannot be explained by its open chain structure?
(i) Despite having the aldehyde group, glucose does not give Schiff test and 2, 4-DNP test.
(ii) Glucose does not react with sodium hydrogen sulphite to form addition product.
(iii) The pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxyl amine showing the absence of free-CHO group.
The Glycosidic linkages and Peptide linkages are present in:
The optically active tartaric acid is named as tartaric acid because it has a positive
The number of hydroxyl groups in glucose is?
A disaccharide X cannot be oxidised by bromine water. The acid hydrolysis of X leads to a laevorotatory solution. The disaccharide X is
The most common monomer of carbohydrates is
Number of compounds from the following which will not produce orange red precipitate with Benedict solution is........
Glucose, maltose, sucrose, ribose,-deoxyribose, amylose, lactose
L-isomer of tetrose gives positive Schiff’s test and has two chiral carbons. On acetylation ‘X’ yields triacetate. ‘X’ also undergoes following reactions.
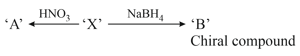
Which of the following will give red ppt in Benedict solution?
The ratio of oxygen and carbon atoms in lipid molecules is:
Which of the following statements is correct ?
The amount of sucrose needed to produce mole of glucose using acid hydrolysis is
Name the reagent and condition required for carrying out of the following reaction
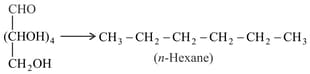
Giving '' Symbol for true statement and '' symbol for false statement, select correct option.
(i) Most naturally occurring amino acids have L-configuration
(ii) ribose sugar is present in
(iii) Amylose is water insoluble component made up of glucose units
(iv) All monosaccharides are non-reducing sugars.
