Enzymes
Enzymes: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Enzymes, Oxidoreductase, Maltase and, Mechanism of Enzymatic Action
Important Questions on Enzymes
The enzyme that converts glucose into ethylalcohol and carbon dioxide is
Enzyme that catalyses hydrolysis of maltose into glucose is knowns as amylase.
Enzyme that catalyses hydrolysis of maltose into glucose is knowns as _____ .
Enzyme having different molecular arrangement but similar functions is
Or
Enzymes which are slightly different in molecular structure but can perform identical activity are called
_____ enzymes catalyse the oxidation of one substrate with simultaneous reduction of another substrate.
Which of the following terms are correct about enzyme?
Name the forces involved in holding the drugs to active sites of enzyme.
Explain lock and key fitting of substrate and enzyme.
What does A represent in the following graph showing enzymatic activity?
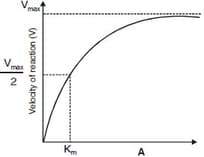
The enzyme catalysing conversion of glucose into alcohol is
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
I. The cell wall of plants is made up of homopolysaccharides while the cell wall of fungi is made up of heteropolysaccharides.
II. The function of an enzyme will stop if its tertiary structure is destroyed.
III. The cytoplasm contains r-thymidylic acid and d-uridylic acid as building blocks of nucleic acids.
IV. Arachidonic acid has 20 carbon atoms including the carboxyl carbon.
Some drugs interact with enzymes and make the biologically inactive. Such drugs are called
