Stereoisomerism
Stereoisomerism: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Optical Isomerism, Stereoisomerism, Geometrical Isomerism, Enantiomers, Diastereomers, Racemic Mixture, Types of Stereoisomerism, Configurational Isomerism and, Conformational Isomerism in Ethane
Important Questions on Stereoisomerism
What is sawhorse projection formula for conformers?
Explain how the different conformations of ethane can be obtained.
Explain the ring strain in cyclopropane molecule.
A molecule of cyclobutane adopts a _____ conformation to minimise torsional strain.
Describe the conformational form of cyclobutane.
Write the formula to calculate the specific rotation of an optically active compound.
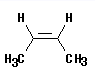
Name the following alkene as per the nomenclature.
Define configurational isomerism.
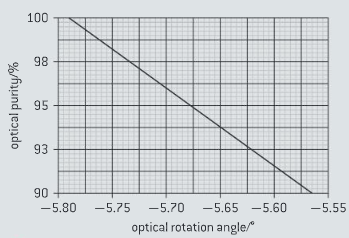
A solution of trans--phenylcyclohexanol was analysed by polarimetry. At a certain concentration, the rotation angle of the solution was . Using the calibration curve in the below figure, determine the optical purity of the sample.
Explain how a polarimeter can be used to identify enantiomers?
Trans--phenylcyclohexanol is used as a chiral auxiliary in the synthesis of anticancer drugs such as Taxol. The structure of one enantiomer of trans--phenylcyclohexanol is given in figure.
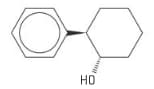
Draw the structural formula of the second enantiomer of trans--phenylcyclohexanol.
Baccatin is the name of a biologically active compound, that can be isolated from the Pacific yew tree, Taxus bervifolia. Together with -deacetylbaccatin, it is a precursor of the anticancer drug Taxol. Baccatin can be converted into -deacetylbaccatin by the following reaction:
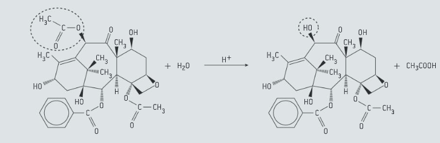
Deduce the number of chiral carbon atoms in the molecule of baccatin .
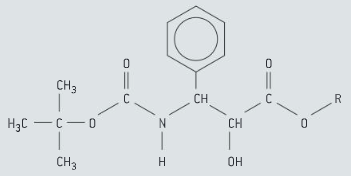
Taxotere (docetaxel) is an anticancer drug that can be synthesised using chiral auxiliaries. A fragment of its structure is shown in figure, deduce the number of possible stereoisomers of this structural fragment.
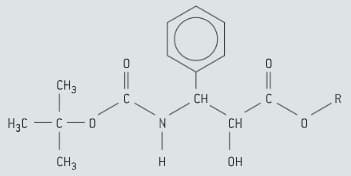
Taxotere (docetaxel) is an anticancer drug that can be synthesised using chiral auxiliaries. A fragment of its structure is shown in figure, identify with asterisks (*) two chiral centres in this structural fragment.
Parexotine, whose structure is shown below, is a drug prescribed to people suffering from mental depression.
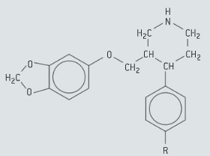
Identify the two chiral carbon atoms with asterisks (*).
Chirality plays an important role in the action of drugs. Describe the composition of a racemic mixture.
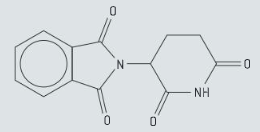
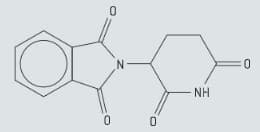
Chirality plays an important role in the action of drugs. Using an asterisks (*) ,identify the chiral carbon atom in a copy of the structure of thalidomide.
Explain the difference between conformation and configuration necessary condition for geometrical isomerism.
