Triangle and its Types
Triangle and its Types: Overview
This topic defines triangles and their classification on the basis of its sides, such as scalene, isosceles and equilateral triangles. Angle-based classification of the same, such as acute, obtuse and right-angle triangles is also mentioned here.
Important Questions on Triangle and its Types
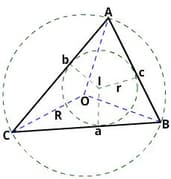
The sides of a triangle are , and . The radius of its incentre is?
is a right-angled triangle, right-angled at . A circle is inscribed in it. The lengths of the two sides of triangle containing the right angle are and respectively. Find the radius of the incircle in .
The incentre of the triangle with vertices is
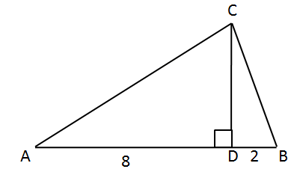
is a right angled triangle. If then find .
If the altitude of a triangle is , its area is and its base is then find .
If the altitude of an equilateral triangle when its equal sides are given as is then find .
Every triangle has altitudes, one from each vertex.
The medians divide the triangle into smaller triangles of equal area.
The orthocenter is located inside the triangle in _____ triangle. (Acute/Right)
Given: is the altitude, . If then find .
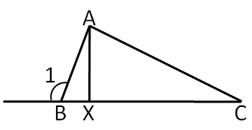
Given: is the altitude, . If is then find
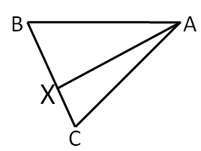
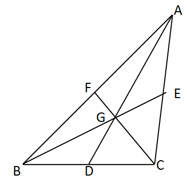
is the centroid of triangle and . If the length of is then find .
The centroid of a triangle is the point at which its three medians intersect.
In the median and passes through the point . If then find (in ) (correct up to one decimal place)
In the median and passes through the point . If then, find (in ).
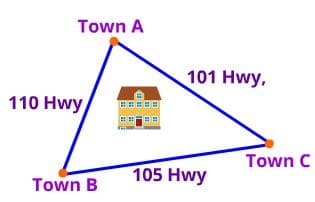
Town A, Town B and Town C are connected by three highways. The government wants to set up a police station to check crimes on the highway. What is the best location for the police station so that it is equidistant and easier to access from the highway?
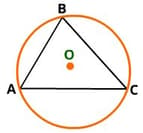
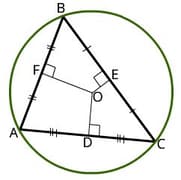
Which point of concurrency is represented by O?
If O is the circumcentre of the triangle then
Identify the circum circle in the figure given above