Assumptions of Kinetic Theory of Gases
Assumptions of Kinetic Theory of Gases: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Ideal Gas Assumptions, Random Motion of Gas Molecules, Negligible Self Volume of Molecules, Large Number of Gas Molecules, Elastic Collisions between Molecules and, Molecules Obey Laws of Motion
Important Questions on Assumptions of Kinetic Theory of Gases
Determine the volume of mole of any gas at S. T. P., assuming it behaves like an ideal gas.
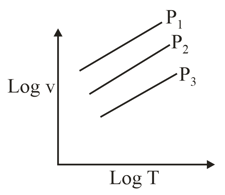
Which of the following order of pressure is correct?
The saturated water vapour pressure on a planet is, . Determine the vapour density .
Choose the correct statement(s):
Using the assumptions made in kinetic theory of gases, derive an expression for pressure acting on the wall of a container by an ideal gas.
Volume of a real gas is negligible as compared to the volume of the container.
The collision between the molecules of an ideal gas is perfectly elastic.
Which one of the following correctly defines an ideal gas?
The collision between molecules of gas with each other and the container of the wall are assumed to be
If volume occupied by Molecules are negligible, then what will be the pressure Exerted by one mole of Gas at
Write the expression of the ideal gas equation.
If volume occupied by molecules is negligible, then what will be the pressure exerted by one mole of at is .
Self volume of molecules is negligible in comparison to total volume of gas contained in a pot.
State the assumption regarding the volume of gas molecules to consider the gas as an ideal gas.
For gas to be ideal gas, it is assumed that the _____ of the molecules is negligibly small compared to the volume occupied by the gas.
For a gas to be “ideal”,the gas particles must have negligible volume.
A sample of an ideal gas occupies a volume at pressure and absolute temperature . The mass of each molecule is , then the density of the gas is
A gas diffuse times as fast as hydrogen. Its molecular weight is
The average intermolecular distance is considerably small as compared to the diameter of the molecule.
State the basic assumptions of kinetic theory of gases.
