Conduction
Conduction: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like The Steady State Heat Flow,Heat Flow and Area of Cross Section,Heat Flow and Temperature Gradient, etc.
Important Questions on Conduction
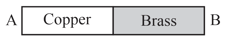
Two rods of copper and brass () of same length and area of cross-section are joined as shown. End is kept a and end at . The temperature at the junction
Two rods, one made of copper and the other made of steel of same length and same cross-sectional area are joined together. The thermal conductivity of copper and steel are and respectively. The free ends of copper and steel are held at and respectively. Calculate the temperature at the junction.
Two plates A and B have thermal conductivities and respectively. They have same surface area and same thickness. They are placed in contact along their surfaces. If the temperatures of the outer surfaces of A and B are kept at and respectively, then the temperature of the surface of contact in steady state is_____ .
When of ice at is mixed with of water at in a container, the resulting temperature is
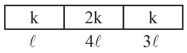
Three identical rods of same metal are connected as shown in figure. In steady state the temperature is
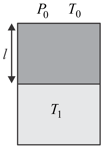
moles of a monoatomic gas at temperature is trapped under a piston having area , length , density and thermal conductivity . and are pressure and temperature of the atmosphere. Find length of the gas column as a function of time. Neglect friction and heat loss through the walls of container and sides of piston.
Why is the mode of heat transfer in Mercury is by conduction although it is a liquid?
Two metallic blocks and of same area of cross-section are connected to each other (as shown in figure). If the thermal conductivity of is then the thermal conductivity of will be : [Assume steady state heat conduction]
of heat is conducted through wall of thickness in . Temperature difference between the two sides of the wall is . The thermal conductivity of the material of the wall is (in ) . Write the value of .
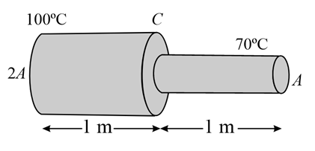
A metal rod of length has cross sectional areas and as shown in the figure. The ends are maintained at temperatures and . The temperature at middle point is___.
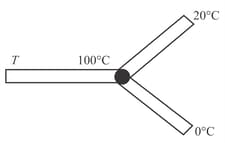
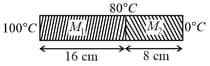
The end of a rod of length is maintained at and the end at . What is the temperature (in ) at a distance of from the end ?
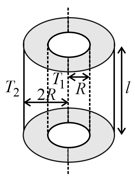
Inner surface of a cylindrical shell of length and of material of thermal conductivity is kept at constant temperature and the outer surface of the cylinder is kept at constant temperature such that as shown in figure. Heat flows from inner surface to outer surface to outer surface radially outward. Inner and outer radii of the shell are and respectively. Due to lack of space this cylinder has to be replaced by a smaller cylinder of length inner and outer radii and respectively and thermal conductivity of material . If rate of radially outward heat flow remains same for same temperature of inner and outer surface i.e. and , then find the value of .
An iron slab and a copper slab having rectangular cross-sections and identical dimensions are welded together end to end. The outer ends of iron and copper slabs are held at and respectively. The thermal conductivities of iron and copper are and , respectively. Then, ignoring convective anc radiative losses, the temperature of the junction is close to
Explain thermal conduction along with the uses of thermal conductors and insulators in daily life.
Two conducting cylinders of equal length but different radii are connected in series between two heat baths kept at temperatures as shown in the figure. The radius of the bigger cylinder is twice that of the smaller one and the thermal conductivities of the materials of the smaller and the larger cylinders are , respectively. If the temperature at the junction of the two cylinders in the steady state is , then is
Why do house made of concrete roofs gets very hot during summer?
The points and are maintained at different temperature. The ratio of the heat transferred through a cross-section of a semi-circular rod to the heat transferred through a cross-section of the straight rod in a given time is,
(Both rods are made of same material and have same cross-sectional area)

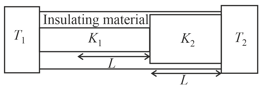
Two bars of unequal length and cross-section have thermal conductivities and . They are connected in series and the junction point is at temperature the one end is maintained at and other end at . What will be the ratio if the ratio of the length of two bars is and the ratio of cross-sectional areas of two bars is ?
Which element is used in nuclear reactor for fuel?