Collisions
Collisions: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Elastic Collision, Coefficient of Restitution, Inelastic Collision, Perfectly Inelastic Collision, Oblique Collision, Head-on Elastic Collision, Head-on Inelastic Collision and, Linear Momentum and Collisions
Important Questions on Collisions
A moving mass of collides elastically with a stationary mass of If be the initial kinetic energy of the moving mass, the kinetic energy left with it after the collision will be :-
Two identical balls each of mass moving on straight track are approaching towards each other with same speed. Final kinetic energy of the two ball system is equal to the total energy loss during collision. is the total kinetic energy of the balls before collision and is after collision and coefficient of restitution is . Then choose the correct options
When both billiard balls collide inelastically, the coefficient of restitution (e) will be
A ball released from a height of , hits the ground and rebound to a height of . The coefficient of restitution of the collision will be
A ball falls from a height such that it strikes the floor of lift at . If lift is moving in the upward direction with a velocity , then velocity with which the ball rebounds after elastic collision will be
A pendulum bob of mass is raised to height and released. At the bottom of its swing, it picks up a mass . To what height will the combined mass rise?
An alpha particle collides elastically with a stationary nucleus and continues moving at an angle of with respect to the original direction of motion.The nucleus recoils at an angle of with respect to this direction. Mass number of this nucleus is
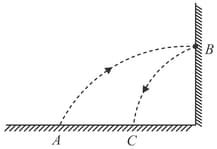
A ball is projected at an angle of with a speed of towards a wall as shown in figure. Ball rebounds such that component of its velocity perpendicular to wall reverses without change in its magnitude while the component of its velocity parallel to the wall remains same. Consider no time lapse in collision. The average acceleration (in ) of the ball throughout the motion is
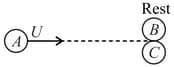
A moving particle collides with a stationary particle of mass times the mass of moving particle, the fraction of its kinetic energy transferred to the stationary particle is
Two objects I and II of mass and collide elastically. If before collision, the object II was at rest and object I was moving. Find the ratio of the final velocity of object I and object II.
A cricket ball is dropped from a building of height and the coefficient of restitution between the ground and ball is . The total distance covered by the ball before it comes to rest is
Two balls and , of masses and respectively collide each other. If the ball A moves with a speed of and collides with ball moving with speed in the opposite direction. After collision if ball A comes to rest and the coefficient of restitution is (one), then the speed of the ball before it collides with ball is
There is an elastic ball which is thrown towards a rigid wall. The work done by the normal reaction exerted by the wall on the ball is:
Which one of the following statement is correct?
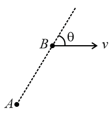
Particle is at rest and particle is moving with constant velocity as shown in diagram at . Find their velocity of separation.
A sphere of mass moving with velocity collides head on elastically with a sphere of mass at rest. After collision their respective velocities are and . The value of :
For head-on collision between two colliding balls of equal radii , the impact parameter is equal to
A particle of mass strikes another particle of same mass at rest elastically. After collision if velocity of one of the particle is , then the other must have a velocity equals to
Two identical masses are kept in contact on a smooth horizontal surface as shown. A third identical mass moving with speed hits the two balls symmetrically and comes to rest. The coefficient of restitution is