Impulse
Impulse: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Linear Impulse, Linear Impulse and Coefficient of Restitution, Linear Impulse of Constant Force, Linear Impulse from F-T Diagrams and, Linear Impulse of Time Varying Force
Important Questions on Impulse
A hammer weighing strikes the head of a nail with a speed of and drives it into the wall. The impulse imparted to the wall is
Two billiard ball each of mass moving in opposite directions with speed collide and rebounds with the same speed. The magnitude of impulse imparted to each ball due to other is
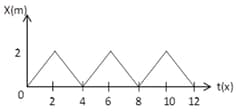
Figure shows the position–time graph of one dimensional motion of a body of mass . What is the time interval between two consecutive impulses received by the body?
A batsman hits back a ball of mass straight in the direction of the bowler without changing its initial speed of . If the ball moves in same straight line, then the impulse imparted by it (in ) is,
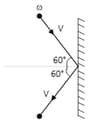
A rigid ball of mass elastically colides a rigid wall at and gets reflected as shown in the figure. Find the impulse imparted by the wall on the ball.
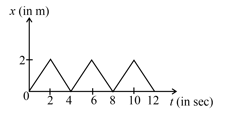
The figure shows the position-time graph of one-dimensional motion of a body of mass The interval between two consecutive impulses received by the body would be
gas molecules each of mass collide with a surface (perpendicular to it) elastically per second over an area with a speed the pressure exerted by the gas molecules will be of the order of
At time sec, a particle of mass has position vector . The impulse of the force during the time interval is
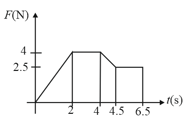
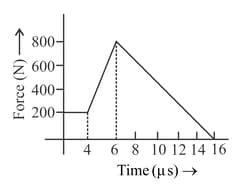
The magnitude of force acting on a body varies with time as shown in the figure. The magnitude of total impulse of the force on the body from to is-
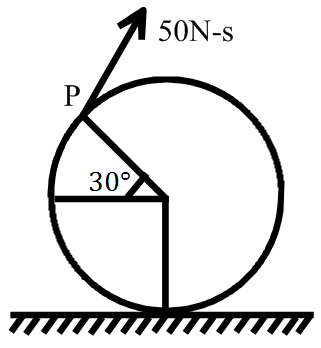
A solid ball of radius and mass lying at rest on a smooth horizontal surface is given an instantaneous impulse of at point as shown. The number of rotations made by the ball about its diameter before hitting the ground is
A particle of mass is moving in a straight line with momentum Starting at time a force acts in the same direction on the moving particle during time interval so that its momentum changes from to Here is a constant. The value of is:
The one which does not represent a force in any context is
A ball of mass m hits a rough floor with a velocity as shown. The coefficient of friction is between the ball and the floor. Answer the questions that follow:
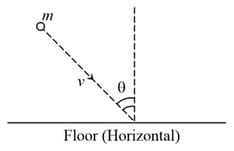
Find out the final velocity of the ball just after the collision. (perfectly inelastic collision)
A ball of mass m hits a rough floor with a velocity as shown. The coefficient of friction is between the ball and the floor. Answer the questions that follow:
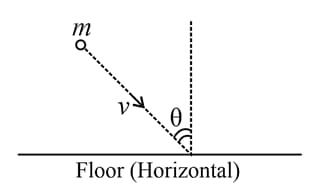
Find out the impulse of the normal on the ball during the collision (for a perfectly inelastic collision)
A ball of mass m hits a rough floor with a velocity as shown. The coefficient of friction is between the ball and the floor. Answer the questions that follow:
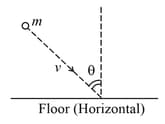
If the collision is perfectly inelastic, the angle made by the velocity of the ball with the horizontal after the collision is
A body of mass 10 kg is acted upon by a given equation Newton. The initial velocity of the body is 10 m/s. The velocity of the body after 5 sec is
At time t second, a particle of mass 3 kg has position vector metre where . The impulse of the force during the time interval is
A body of mass 5 kg is acted on by a net force F which varies with time t as shown in graph, then the net momentum in SI units gained by the body at the end of 10 seconds is
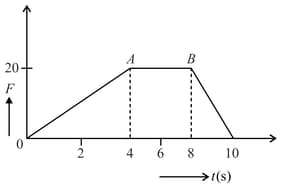
A body of has an initial speed . A force acts on it for in the direction of motion. The force-time graph is shown in figure. The final speed of the body after is