Hooke's Law and Modulus of Elasticity
Hooke's Law and Modulus of Elasticity: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Hooke's Law, Young's Modulus of Elasticity 'Y', Young’s Modulus of Elasticity of Material of a Metallic Wire & Increment of Length Due to Own Weight etc.
Important Questions on Hooke's Law and Modulus of Elasticity
A student performs an experiment to determine the Young’s modulus of a wire, exactly long, by Searle’s method. In a particular reading, the student measures the extension in the length of the wire to be with an uncertainty of at a load of exactly . The student also measures the diameter of the wire to be with an uncertainty of . Take (exact). The Young’s modulus obtained from the reading is
Same tension is applied to the following four wires made of same material. The elongation is longest in
The bulk modulus of a liquid is . The pressure required to reduce the volume of liquid by is :
A steel wire of cross-sectional area can withstand a maximum strain of . Young's modulus of steel is . The maximum mass this wire can hold is,
A rod of length and coefficient of linear expansion per degree is placed symmetrically between fixed walls separated by . Young's modulus of the rod is . If the temperature is increased by then the stress developed in the rod is (in )
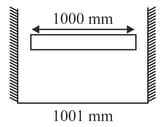
The backlash error can be eliminated in Searle's experiment, by rotating screw in
The translational kinetic energy of molecule of a gas, at temperature is
A copper and a steel wire of same diameter are connected end to end. A deforming force is applied to this composite wire which causes a total elongation of . The two wires will have:
The area of cross-section of a wire of length is Find the increase in its length when it is loaded with The Young's Modulus of material of wire is
A wire of length suspended vertically from a rigid support is made to suffer extension in its length by applying a force Then the work done is
The length of a rod under longitudinal tension is and that under longitudinal tension is . What is the actual length of the rod, in the absence of tensions?
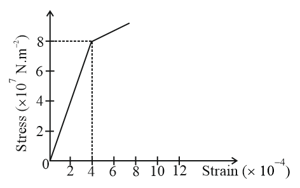
Find the Young's modulus of the wire whose stress-strain curve is as shown in the following figure:
One end of a wire of radius and length is fixed and the other end is twisted through an angle of The angle of shear is
The ratio of shearing stress to the corresponding shearing strain is called the modulus of _____.
The dimensional formula of modulus of rigidity is .
State the units and dimensions of modulus of rigidity.
The dimensional formula of modulus of rigidity is
A rubber ball is taken to a deep lake and its volume changes by . The bulk modulus of rubber is nearly
A steel rail of length and area of cross-section is prevented from expanding along its length while the temperature rises by . If coefficient of linear expansion and Young's modulus of steel are and respectively, the force developed in the rail is approximately:
The pressure that has to be applied to the ends of a steel wire of length 10 cm to keep its length constant when its temperature is raised by 100oC is :
(For steel Young's modulus is 2 x 1011 N m-2 and coefficient of thermal expansion is 1.1 x 10-5 K-1)
