Center of Mass
Center of Mass: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Centre of Mass, Centre of Mass of Continuous Bodies, Centre of Mass of Two Particles, Centre of Mass of Symmetrical Bodies and, Centre of Mass of More than Two Particles
Important Questions on Center of Mass
Two spherical bodies of mass and and radii and respectively are released in free space with initial separation between their centres equal to . If they attract each other due to gravitational force only, then the distance covered by the smaller body just before collision is–
If the resultant of all the external forces acting on a body be zero, the centre of mass of the system
Two bodies of different masses and are moving with velocities and towards each other due to mutual gravitational attraction. Then the velocity of the centre of mass is
For a bangle, the centre of mass lie outside the body.
The center of mass of a system of particles does not depend upon force acting on particle.
Two particles A and B initially at rest, move towards each other, under mutual force of attraction. At an instance when the speed of A is and speed of B is , the centre of mass (CM) remains at rest. This statement is _____. Choose from (True/False).
Centre of mass of rectangular lamina lies on the point of intersection of the _____.
The centre of mass of a body lies always inside the body.
For which of the following does the centre of mass lie outside the body ?
In the figure shown the system is at rest initially. Two persons and of masses each move with speeds and respectively towards each other on a plank lying on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure. Plank travels a distance of towards right direction in (Here and are given with respect to the plank). Then:
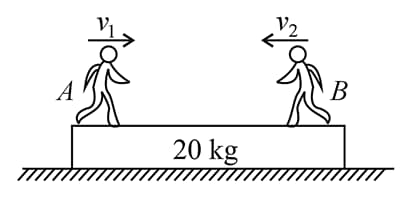
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
On a horizontal frictionless frozen lake, a girl and a box are connected to each other by means of a rope. Initially, they are apart. The girl exerts a horizontal force on the box pulling it towards her. How far has the girl travelled when she meets the box?
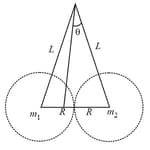
Two identical objects each of radii and masses and are suspended using two strings of equal length as shown in the figure The angle which mass makes with the vertical is approximately
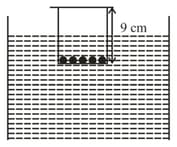
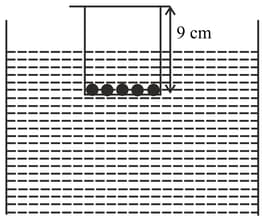
A wide bottom cylindrical massless plastic container of height , has identical coins inside it and is floating on water with inside the water. If we start putting more of such coins on its lid, it is observed that after coins are put, its equilibrium changes from stable to unstable. Equilibrium in floating is stable if the geometric center of the submerged portion is above the center of mass of the object). The value of is closest to
The centre of mass of solid hemisphere of radius is from the centre of the flat surface. Then value of is _________ .
Figure below shows a shampoo bottle in a perfect cylindrical shape
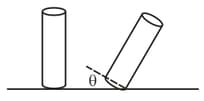
In a simple experiment, the stability of the bottle filled with different amount of shampoo volume is observed. The bottle is tilted from one side and then released. Let the angle depicts the critical angular displacement resulting in the bottle losing its stability and tipping over. Choose the graph correctly depicting the fraction of shampoo filled ( corresponds to completely filled) vs the tipping angle .
A wide bottom cylindrical massless plastic container of height has identical coins inside it and is floating on water with inside the water. If we start putting more of such coins on its lid, it is observed that after coins are put, its equilibrium changes from stable to unstable. Equilibrium in floating is stable if the geometric center of the submerged portion is above the center of mass of the object). The value of is closest to
Give an example to show that the following statement is false. 'Any two forces acting on a body can be combined into single force that would have same effect'.
Two heavenly bodies and , not far off from each other are seen to revolve in orbits
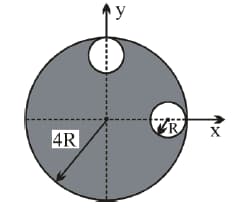
From the circular disc of radius two small discs of radius are cut off. The center of mass of the new structure will be
Consider a two block system having masses and , as shown in the figure. If block A is pushed towards the centre of mass through a distance , by what distance should the block be moved so as to keep the centre of mass at the same position.

