Friction Acting on Multiple Surfaces
Important Questions on Friction Acting on Multiple Surfaces
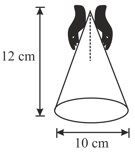
With two hands, you hold a cone motionless upside down, as shown in figure. The mass of the cone is and the coefficient of static friction between your fingers and the cone is What is the minimum normal force (in ) you must apply with each hand in order to hold up the cone? Consider only translational equilibrium.
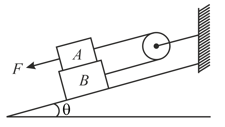
Block has a mass of and block a mass of The coefficients of friction between all surfaces of contact are and Knowing that and that the magnitude of the force applied to block is determine the acceleration of block (in ).
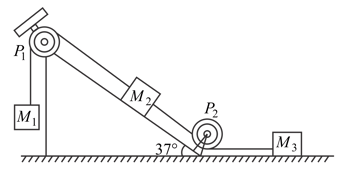
In the figure shown, block and weigh undefined and undefined respectively. The coefficient of sliding friction between any two surfaces is undefined is held at rest by a massless rigid rod fixed to the wall while and are connected by a string passing around a frictionless pulley. Find the force needed (in ) to drag along the horizontal surface to the left at a constant speed. Assume the arrangement shown in the figure is maintained all through.
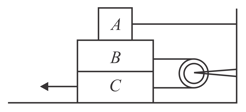
The maximum value of the mass of block (in undefined) so that neither nor moves is (Given that mass of is undefined and that of is undefined Pulleys are smooth and friction coefficients between and and between and horizontal surface is ( undefined)
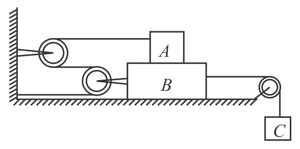
Masses and are connected by light strings which pass over pulleys and as shown. The masses move such that the string between and is parallel to incline and the string between and is horizontal, The coefficient of kinetic friction between masses and the surface is The angle of inclination of plane is to the horizontal. If the mass moves downward with uniform velocity, find the tension in the horizontal string (in ). (Given )
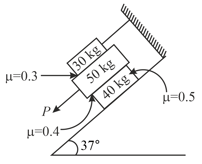
The three flat blocks in the figure are positioned on the incline and a force parallel to the inclined plane is applied to the middle block. The upper block is prevented from moving by a wire which attaches it to the fixed support. The masses of three blocks in and coefficient of static friction for each of the three pairs of contact surfaces are shown in the figure. If the maximum value which force may have before slipping takes place anywhere is found to be . Find the value of .
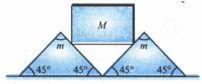
Two wedges, each of mass , are placed next to each other on a flat horizontal floor. A cube of mass is balanced on the wedges as shown in the figure. Assume no friction between the cube and the wedges, but a coefficient of static friction between the wedges and the floor. What is the largest ratio of , so that the system can be balanced without the motion of the wedges?
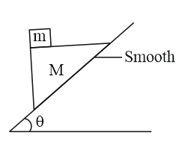
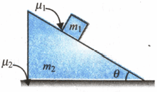
A block of mass is placed on a wedge of an angle , as shown. The block is moving over the inclined surface of the wedge of mass . The friction coefficient between the block and the wedge is , whereas it is between the wedge and the horizontal surface. If the minimum value of , so that the wedge remains stationary on the surface is found to be . Find the value of . Take, .
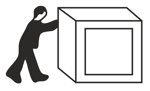
A man of mass is pushing a heavy box on a flat floor. The coefficient of kinetic and static friction between the floor and the box is and the coefficient of static friction between the man's shoes and the floor is If the man pushes horizontally (see figure), what is the maximum mass (in ) of the box he can move?
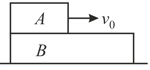
A block of mass is placed over a plank of mass Plank is placed over a smooth horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between and is . Block is given a velocity towards the right. Find acceleration (in ) of relative to
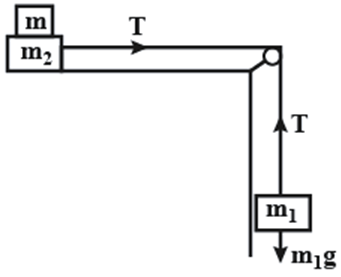
Block , of mass , rests on the block , with mass , which in turn is on a horizontal tabletop (as shown in the figure). The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the tabletop is and the coefficient of static friction between block and block is . A light string attached to the block passes over a frictionless, massless pulley and the block is suspended from the other end of the string. What is the largest mass (in ) that block can have so that blocks and still slide together when the system is released from rest?
A block of mass is projected at with a horizontal velocity on a stationary plank which starts moving with a constant horizontal acceleration . If coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and plank, find
(a) The magnitude and direction of the frictional force on the block at .
(b) time after the block comes to rest relative to the plank.
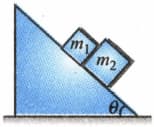
A block of mass and another mass are placed together (see figure) on an inclined plane with the angle of inclination . Various values of are given in the List . The coefficient of friction between the block and the plane is always zero. The coefficient of static and dynamic friction between the block and the plane is equal to . In List expressions for the friction on the block are given. Match the correct expression of the friction in List with the angles given in List , and choose the correct option. The acceleration due to gravity is denoted by .
[Useful information: , , ]
| List- | List- | ||
Two masses and connected to inextensible string over a frictionless pulley, are moving as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction of horizontal surface is The minimum weight that should be put on top of to stop the motion is
Find the maximum force that the man can exert on the rope so that the board does not slip on the floor. The friction coefficient between the board and the floor shown in figure is
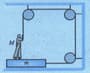
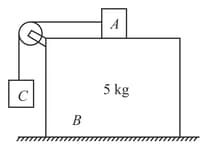
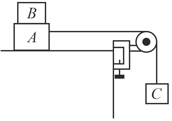
Block weighs and blocks weight The coefficient of kinetic friction is for all surfaces. Find the force to slide at a constant speed when
(a) is held at rest and
(b) and are connected by a light cord passing over a smooth pulley as shown in figure (a-b), respectively.
A triangular prism of mass with a block of mass placed on it is released from rest on a smooth inclined plane of inclination . The block does not slip on the prism. Then
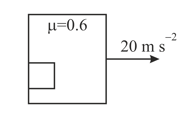
A box is accelerating with acceleration . A block of mass placed inside the box and is in contact with the vertical wall as shown. The friction coefficient between the block and the wall is and take . Then
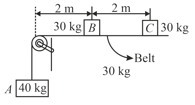
Two blocks rest on a massless belt which passes over a fixed pulley and is attached to a block. If coefficient of friction between the belt and the table as well as between the belt and the blocks and is and the system is released from rest from the position shown, the speed with which the block falls off the belt is
All the blocks shown in the figure are at rest. The pulley is smooth and the strings are light. Coefficient of friction at all the contacts is . A frictional force of acts between and . The block is about to slide on block . The normal reaction and frictional force exerted by the ground on the block is