Plastids
Plastids: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Plastids, Structure of a Chloroplast, Thylakoids, Functions of Chloroplast, Grana and, Stroma Matrix
Important Questions on Plastids
Which kind of plastid is more common in flowers and fruits?
Draw a well-labelled diagram of mitochondria and chloroplast.
Write any two differences between mitochondria and chloroplast.
What is common between chloroplasts, chromoplasts and leucoplasts?
Why are chloroplasts essential for the growth and survival of plants and photosynthetic algae?
Light energy is absorbed by photosynthetic pigments and converted into ATP by chlorophyll.
Chloroplast produces NADPH and molecular oxygen (O2) by _____ of water.
Chloroplasts are the sites for respiration.
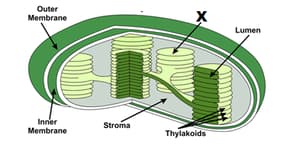
In the above diagram the structure labelled as 'X' indicates Granum.
Chlorophylls are greenish pigments which contain a _____ ring with a central magnesium ion (Mg2+).
Why are the chloroplasts believed to have evolved in eukaryotic cells from free-living bacteria?
_____ is a green coloured plastid that takes part in the synthesis of carbohydrates.
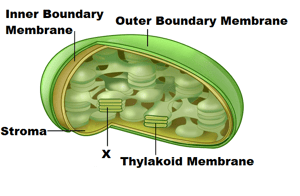
In the above diagram, the structure labelled as 'X' indicates Thylakoid Lumen.
Thylakoids are responsible for the conversion of NADP+ to _____.
Thylakoids are the site of the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis.
The _____ is captured by the membrane of thylakoids.
Thylakoids are found commonly in plastids of
Select the plastids out of the following:
Which of the following organelle contain its own DNA and ribosome?
