Cardiac Cycle
Cardiac Cycle: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as P-wave in Electrocardiogram, QRS complex in Electrocardiogram, T-wave in Electrocardiogram, Cardiac Cycle, Joint Diastole, Atrial Systole, Ventricular Systole, Cardiac Output, etc.
Important Questions on Cardiac Cycle
Match the following
| List - I | List - II | ||
| a | Enlarged wave | i | Hyper calcimia |
| b | Prolonged interval | ii | Tachy cardia |
| c | Prolonged interval | iii | Brady cardia |
| d | Shortened interval | iv | Myocardial infraction |
| v | Enlarged atria |
Which one of the following is a matching pair?
a) Lubb - sharp closure of AV valves at the beginning of ventricular systole
b) Dub - sudden opening of semilunar valves at the beginning of ventricular diastole
c) Pulsation of the radial artery - valves in the Arteries
d) Initiation of the heart beat - Purkinje fibres
During ventricular systole in a mammalian heart the
P wave of ECG indicates:
1. Activation of SA node.
2. Depolarization of atrial muscles.
3. Spread of excitation from AV node to Purkinje fibres.
4. Repolarisation of atria and depolarization of ventricles.
The diagram given here is the standard of a normal person. The - wave represents the?
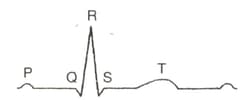
In a standard which one of the following alphabets is the correct representation of the respective activity of the human heart?
In , what is represented by -wave, complex and -wave respectively?
In the given ECG graph, the T-wave represents
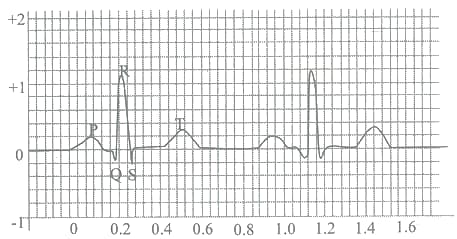
The systolic arterial blood pressure is
In electrocardiogram, X and Y-axis represent
Father of Electrocardiography is
The working of heart is recorded by
A graphic record of electrical variations produced by the heart during one heart beat or cardiac cycle is called
If ECG reflects flat T waves, it means the person may not be suffering from
