Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular Forces: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as intermolecular forces, london dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, dipole-induced dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding.
Important Questions on Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction and repulsion between interacting particles that will include :
A. dipole-dipole forces.
B. dipole-induced dipole forces.
C. hydrogen bonding.
D. covalent bonding.
E. dispersion forces.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Which of the following has maximum dispersion forces of attraction?
The type of the bond formed during the hydration of cation is
When a cation gets hydrated, normally the bond formed between cation and water molecule is:
Dipole - induced dipole interactions are present between which of the following pairs?
Explain London dispersion forces.
The dipole-dipole interaction energy between rotating polar molecules is proportional to, where '' is the distance between polar molecules.
Identify the nature of intermolecular force acting between and molecules.
Hydrogen bonding is found in:
Define hydrogen bonding.
An example of dipole-dipole force is:
London forces are long distance forces.
Dispersion forces are also known as _____.
Define intermolecular forces among particles.
What are dipole-induced dipole forces?
Three types of potential energy due to attractive interaction between two species and are represented by the curves and in the figure below.
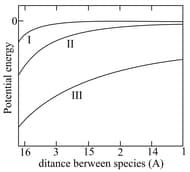
Consider the dominating interaction between non-rotating species for , and . The correct assignment of the ... interactions
to the types , and is:
Explain the type of bonding in water ?
Describe the dipole-induce dipole forces.
Glaciers always melt at the first.
Hydrogen bond is a special case of
