Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures of Gases, Derivation of Dalton's Law, and Partial Pressure in Terms of Mole Fraction.
Important Questions on Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure
A gaseous mixture was prepared by taking equal mole of If the total pressure of the mixture was found 1 atmosphere, the partial pressure of the nitrogen in the mixture is:
If 500ml of gas A at 400 torrs and 666.6 ml of B at 600 torrs are placed in a 3 liter flask, the pressure of the system will be
If 500ml of gas A at 400 torr and 666.6 ml of B at 600 torr are placed in a 3 litre flask, the pressure of the system will be
A gaseous mixture of moles of , moles of , moles of and moles of is contained in a vessel. Assuming that gases are ideal and the partial pressure of is atm, total pressure is
If and are mole fraction, pressure fraction and volume fraction, respectively, of a gaseous mixture, then
each of , and are present in a container exerting pressure at . The pressure in atm exerted by each of and in the second container of same volume and temperature is
A mixture of nitrogen and water vapour is admitted to a flask that contains a solid drying agent. Immediately after admission, the pressure in the flask is . After standing for some hours, the pressure reaches a steady value of . Calculate the mole percent of water vapour in the original mixture.
A mixture of and gases in a cylinder contains of and of . If the total pressure of the mixture of the gases in the cylinder is bar, the partial pressure of is:
[Use atomic masses (in ): ]
Given $\mathrm{p}_{\mathrm{CC}_{4}}^{0}=100$ torr, $\mathrm{p}_{\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}}^{0}=300$ torr
What will be total pressure (in torr) for immiscible mixture after opening the valve? Give your answer after
dividing by .
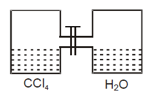
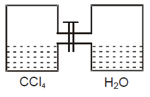
60 g of gaseous is mixed with 28 g of carbon monoxide. The pressure of the resulting gaseous mixture is 3 atm. The partial pressure in atm of in the mixture is
If the ratio of masses of and gases confined in a vessel is , then the ratio of their partial pressure would be
To which of the followings the Dalton's law of partial pressures is not applicable?
Given a mixture with mole of gas A and moles of gas B. Total pressure is at temperature in a vessel of volume . Then, find (R universal gas constant)
The density of a mixture of and is at STP. Calculate partial pressure of
Gaseous benzene reacts with hydrogen gas in presence of a nickel catalyst to form gaseous cyclohexane according to the reaction,
A mixture of and excess has a pressure of 60 mm of Hg in an unknown volume. After the gas had been passed over a nickel catalyst and all the benzene converted to cyclohexane, the pressure of the gas was 30 mm of Hg in the same volume at the same temperature. The fraction of (by volume) present in the original volume is
A sample of air contains only and . It is saturated with water vapours and the total pressure is 640 torr. The vapour pressure of water is 40 torr and the molar ratio of is 3 : 1. The partial pressure of in the sample is
Statement-1: In an empty container, equal weights of methane and hydrogen are mixed at . The fraction of the total pressure exerted by methane is
Statement-2:
Statement = Considering van der Waals' equation of state for a real gas the constant 'a' for is less than that for
Explanation = The molar mass of is almost twice that of
of gas is introduced to an evacuated flask at . The pressure of the gas is . Now of another gas is introduced in the same flask. The total pressure becomes . Calculate the volume of the vessel if is .
A flask of capacity one litre contains at & . A spark is passed through until all the is decomposed into & . Calculate the pressure of gases left at .
