Coulomb's Law
Coulomb's Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as electrostatic force between two charges in vacuum, permittivity of vacuum, dielectric constant of a medium, Coulomb's law, and Coulomb's law in vector form.
Important Questions on Coulomb's Law
Two protons move parallel to each other, keeping distance r between them, both moving with same velocity . Then the ratio of the electric and magnetic force of interaction between them is
Two fixed point charges units are separated by a distance ‘a’. Where should the third point charge be placed for it to be in equilibrium?
How does the coulomb force between two point charges depend upon the dielectric constant of the intervening medium?
A charge is situated at a distance '' away from both the sides of a grounded conducting '' shaped sheet as shown in the figure.
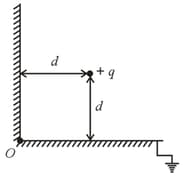
The force acting on the charge is
The force of attraction between two charges and is . Find the distance of separation (in metre):
As per Coulomb's law, the force of attraction or repulsion between two point charges is directly proportional to the
The Dielectric constant of a medium is the ratio of the permittivity of the substance to the permittivity of free space
Two point charges are kept in air with a separation between them. The force between them is , if half of the space between the charges is filled with a dielectric of dielectric constant and the force between them is , if of the space between the charges is filled with dielectric of dielectric constant. Then is
Three particles of charges and are kept fixed on the -axis at point and respectively. The magnitude of the electric force acting on a charge placed at (Assume )
When distance between two-point charges is increased by , the force of interaction
Two point charges and repel each other with a force of . If a charge of is added to each of them, then the magnitude of the force between them and nature of force is/are:
The force between two small charged spheres having charges of and placed apart in air is _____.
Two point charges A and B, having charges and respectively, are placed at certain distance apart and force acting between them is . If charge of A is transferred to B, then the force between the charges becomes
Two point charges and repel each other with a force of . If a charge of is added to each of them, then the force between them will become:
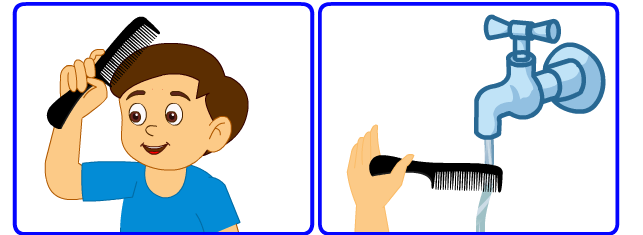
Ravi rubs a plastic comb on his dry hair and then places it near a water stream. The stream of water is seen to bend towards the plastic comb. Which force is behind this event?
The separation between two point charges and is . The sum of the two charges is and they repel each other by a force of . Find the value of the two charges.
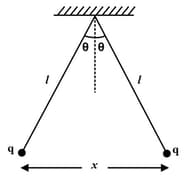
Two small identical balls each of mass and charge are suspended same point by silk cords (each cord is of length ) as shown in fig. separation between charges is and angle between cords . Calculate the value of assuming system to be in equilibrium.
Two identical spherical conductors and carry equal like charges and repel each other by a force when placed at a certain distance apart. Another identical conductor which is uncharged is made into contact with then with and removed away from and . Find the new force acting between and .
Two identical metallic spheres are charged with and . If they are brought into contact and then kept at the same separation as earlier, then find the ratio of forces in final and initial situations.