Thermal Conductivity
Thermal Conductivity: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Coefficient of Thermal Conductivity, Heat Flow through Slabs in Series, Heat Flow through Cylindrical Bodies & Heat Flow through Spherical Bodies etc.
Important Questions on Thermal Conductivity
Which one is having the lowest thermal conductivity?
What is the Searle's apparatus?
What is Searle's method for thermal conductivity?
Two rods of the same length and diameter having thermal conductivities and are joined in parallel. The equivalent thermal conductivity of the combination is
The lengths and radii of two rods made of same material are in the ratios and , respectively. If the temperature difference between the ends for the two rods be the same, then in steady state, the amount of heat flowing per second through them will be in the ratio,
A partition wall has two layers of different materials and in contact with each other. They have the same thickness but the thermal conductivity of layer is twice that of . At steady state, if the temperature difference across the layer is , then the corresponding temperature difference across the layer is
of heat flowing through a rod of iron per second. When the rod is cut down to pieces then what will be the heat flowing through each piece per second having the same differential temperature (temperature gradient)?
The two ends of a metal rod are maintained at temperatures and The rate of heat flow in the rod is found to be If the ends are maintained at temperatures and the rate of heat flow will be:
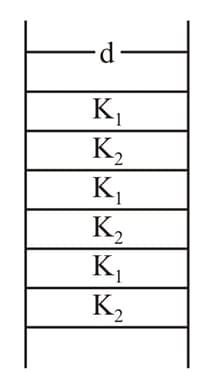
A wall consists of alternating blocks with length and coefficient of thermal conductivity and The cross sectional area of the blocks are the same. The equivalent coefficient of thermal conductivity of the wall between left and right is,
Consider a compound slab consisting of two different materials having equal thicknesses, equal cross-section area and thermal conductivities and respectively. If they are connected in series combination, the equivalent thermal conductivity of the slab is-
If two metallic plates of equal thickness, equal cross-section area and thermal conductivities and are put together face to face (series combination) and a common plate is constructed, then the equivalent thermal conductivity of this plate will be-
Two rods having thermal conductivities in the ratio of and having an equal length and equal cross-section are joined by face to face(series combination). If the temperature of the free end of the first rod is and the free end of the second rod is then the temperature of the junction, is-
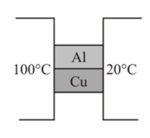
Two metal cubes with -edges of copper and aluminium are arranged as shown in figure
The ratio of the thermal current carried by the copper cube to that carried by the aluminium cube is: -
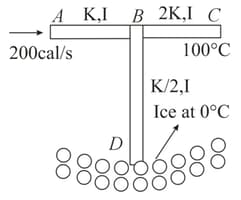
Three rods and of same length and cross-sectional area are arranged as shown. The end is immersed in ice whose mass is and is at . The end is maintained at . Heat is supplied at constant rate of . Thermal conductivities of and are and , respectively. Time after which whole ice will melt is
A copper rod of length and an iron rod of length having the same areas of cross section are connected in series. Thermal conductivities of copper and iron are respectively and units. The equivalent conductivity of the composite bar in unit is ____.
A long rod has one end at and other end at a high temperature. The coefficient of thermal conductivity varies with distance from the low temperature end as, , where SI unit and . At what distance from the first end, the temperature will be ? The area of cross-section is and rate of heat conduction is .
The diameter of a rod is given by where is a constant and is the distance from one end. If the thermal conductivity of the material is what is the thermal resistance of the rod if length is .
A wall has two layers and each made of different materials. Both the layers have the same thickness. The thermal conductivity of material is twice of . Under thermal equilibrium the temperature difference across the layer is . The temperature difference across layer is
Water is completely filled in the spherical cavity of radius of a thick spherical shell of inner and outer radii and respectively as shown. The initial temperature of water is and the surrounding temperature is The thermal conductivity of the spherical shell varies as where is the distance from the centre of shell and is a constant. The time required to decrease the temperature of water from to is density of water, specific heat of water
In an Air conditioner compartment of a train if a material of thermal conductivity and thickness is required to fullfill the purpose. To do so there is a need of two glass each of thickness with air gap of between them. If thermal conductivity of glass and air are and then the value of is: