Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Solutions, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Solutions, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 8: Solutions, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Chemistry solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Solutions, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with Hints & Solutions
of Benzoic acid is dissolved in of Acetone and of Benzene separately. Boiling point of the solution in Acetone increases by while that of, in the Benzene increases by for Acetone and Benzene are and respectively. Molecular weight of Benzoic acid in Benzene is and in Acetone is . Calculate ?
The elevation in boiling point of a solution of of in of water using the following information, will be (Molecular weight of and ) : (Report the answer in two decimal places)
For a dilute solution containing of a non- electrolyte solute. in of water, the elevation in boiling point at atm pressure pressure is Assuming concentration of solute is much lower than the concentration of solvent, the vapour pressure of ) of the solution is (take
Benzene and naphthalene form an ideal solution at room temperature. For this process, the true statement(s) is (are):
dissociates into and ions in an aqueous solution, with a' degree of dissociation of The ratio of the observed depression of freezing point of the aqueous solution to the value of the depression of freezing point in the absence of ionic dissociation is
Mixture(s) showing positive deviation from Raout's law at is (are)
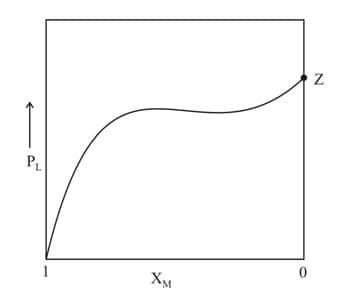
For a solution formed by mixing liquids and the vapour pressure of plotted against the mole fraction of in solution is shown in the following figure. Here and represent mole fractions of and respectively, in the solution. The correct statement(s) applicable to this system is (are):
The plot given below shows curves (where is the pressure and is the temperature) for two solvents and and isomolal solutions of in these solvents. completely dissociates in both the solvents.
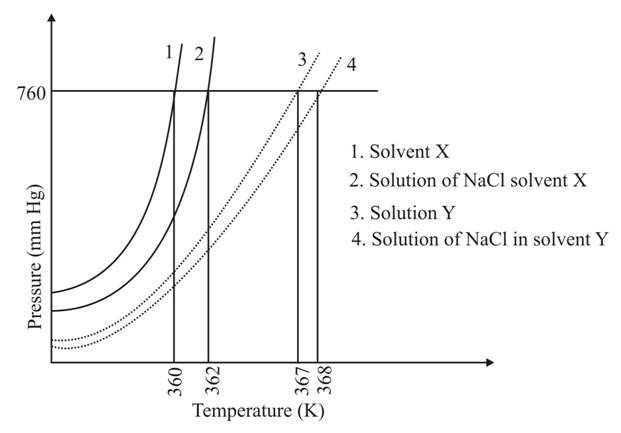
On addition of equal number of moles of a non-volatile solute in equal amount (in ) of these solvents, the elevation of boiling point of solvent is three times that of solvent Solute is known to undergo dimerization in these solvents. If the degree of dimerization is in solvent the degree of dimerization in solvent is:
