Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Current Electricity, Exercise 4: Exercise - 4
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Current Electricity, Exercise 4: Exercise - 4
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 24: Current Electricity, Exercise 4: Exercise - 4 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Current Electricity, Exercise 4: Exercise - 4 with Hints & Solutions
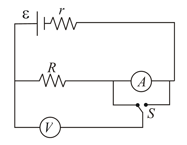
The emf and the internal resistance of the battery shown in figure are and , respectively. The external resistance is . The resistances of the ammeter and voltmeter are and , respectively. (a) Find the readings of the two meters. (b) The switch is thrown to the other side. What will be the readings of the two meters now?
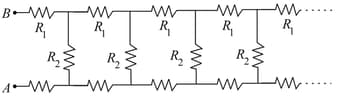
Consider an infinite ladder network shown in the figure. A voltage is applied between points and . If the voltage is halved after each section, find the ratio . Suggest a method to terminate it after a few sections without introducing much error in attenuation.
A nichrome wire of uniform cross-sectional area is bent to form a rectangular loop . Another nichrome wire of the same cross-section is connected to form the diagonal. Find out the ratio of the resistances across and if and.
An electric heater has heating coilsand , when coilis switched on, the water boils in , and when coil is switched on the water boils in . Calculate the time taken by water, to boil if the coils connected in (a) Series and (b) Parallel all switched on.
A rod of length and cross-section area lies along the x-axis between and . The material obeys Ohm's law and its resistivity varies along the rod according to, The end of the rod at is at a potential and it is zero at
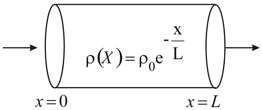
(a) Find the total resistance of the rod and the current in the wire.
(b) Find the electric potential in the rod as a function of .
A galvanometer having divisions provided with a variable shunt is used to measure the current when connected in series with a resistance of and a battery of internal resistance It is observed that when the shunt resistances are respectively, the deflection are respectively and divisions. What is the resistance of the galvanometer? Further, if the full scale deflection of the galvanometer movement require , find the emf of the cell.
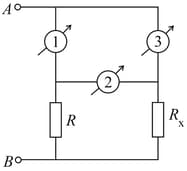
In the circuit shown the three ammeters (marked as 1, 2, 3) are identical, each have a resistance . Between points and there is a constant potential difference of . The first and second ammeter read and , respectively.
(a) What is the reading of third ammeter?
(b) Calculate value of resistance .
(c) Investigate what happens to current if the value of is changed. Show approximately graphical variation of vs .
Note : Reading of ammeter implies current through branch of ammeter.
This question is about a closed electrical black box with three terminals and as shown. It is known that the electrical elements connecting the points inside the box are resistances (if any) in delta formation. A student is provided a variable power supply, an ammeter and a voltmeter. Schematic symbols for these elements are given in part (a). She is allowed to connect these elements externally between only two of the terminals ( or or ) at a time to form a suitable circuit.
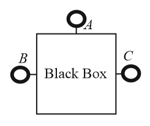
(a) Draw a suitable circuit using the above elements to measure the voltage across the terminals and and the current drawn from power supply as per Ohm’s law.
(b) She obtains the following readings in and for the three possible connections to the black box.
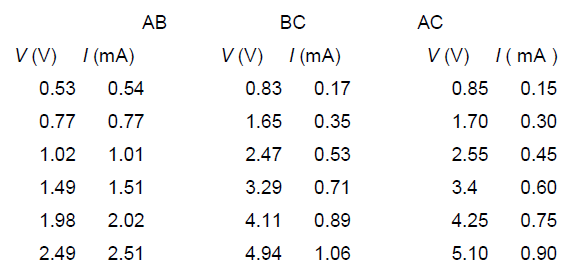
In each case plot (on Y-axis) (on X-axis) on the graph papers provided. Preferably use a pencil to plot. Calculate the values of resistances from the plots. Show your calculations below for each plot clearly indicating graph number.
(c) From your calculations above draw the arrangement of resistances inside the box indicating their values.
