Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Elasticity, Exercise 1: Exercise - 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Elasticity, Exercise 1: Exercise - 1
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 12: Elasticity, Exercise 1: Exercise - 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Elasticity, Exercise 1: Exercise - 1 with Hints & Solutions
Calculate the increase in energy of a brass bar of length and cross-sectional area when compressed with a load of along its length.
(Young’s modulus of brass and ).
When the load on a wire increased slowly from weight to weight, the elongation increases from to . How much work is done during the extension of the wire?
The diameter of a brass rod is and Young’s modulus of brass is . The force required to stretch it by of its length is:
A steel wire is suspended vertically from a rigid support. When loaded with a weight in air, it expands by and when the weight is immersed completely in water, the extension is reduced to . Then relative density of the material of the weight is
Two wires of equal length and cross-section area suspended as shown in the figure. Their Young's modulus are and respectively. The equivalent Young's modulus will be
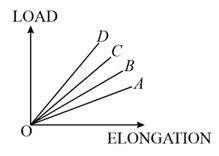
The load versus elongation graph for four wires of the same materials is shown in the figure. The thinnest wire is represented by the line:
A given quantity of a gas is at pressure and absolute temperature . The isothermal bulk modulus of the gas is
A gas undergoes a process in which its pressure and volume are related as . The bulk modulus of the gas in the process is
