Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Viscosity and Surface Tension, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Viscosity and Surface Tension, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 14: Viscosity and Surface Tension, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Viscosity and Surface Tension, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with Hints & Solutions
The following observations were taken for determining surface tension of water by capillary method. Diameter of capillary , rise of water . Using and the simplified relation, , the possible error in surface tension is closest to
Two hail stones with radii in the ratio of fall from a great height through the atmosphere. Then the ratio of their momentum after they have attained terminal velocity is
A spherical ball is dropped in a long column of viscous liquid. Which of the following graphs represent the variation of
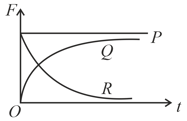
(i) gravitational force with time.
(ii) viscous force with time.
(iii) net force acting on the ball with time.
A small steel ball falls through a syrup at constant speed of . If the steel ball is pulled upwards with a force equal to twice its effective weight, how fast will it move upwards?
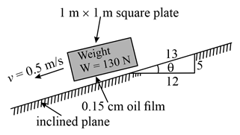
If the approximate viscosity of the oil for the following case is then find :
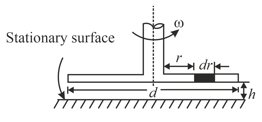
A circular disc of a diameter is slowly rotated in a liquid of large viscosity at a small distance from a fixed surface as shown in the figure. If an expression for torque necessary to maintain an angular velocity is then find .
A small ball bearing is released at the top of a long vertical column of glycerine of height . The ball bearing falls through a height in a time and then the remaining height with the terminal velocity in time . Let and be the work done against viscous drag over this height. Therefore,
