Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 8: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 2: Exercise - 2 with Hints & Solutions
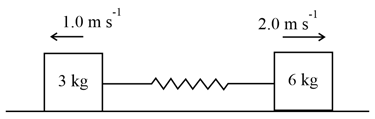
Two blocks of mass and respectively are placed on a smooth horizontal surface. They are connected by a light spring of force constant Initially the spring is unstretched and the indicated velocities are imparted to the blocks. Find maximum extension of the spring in ?
In the figure shown, there is no friction between and ground and between and .
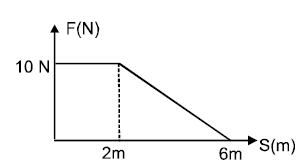
A body of constant mass moves under variable force as shown. If at and velocity of the body is and the force is always along direction of velocity, then choose the incorrect options
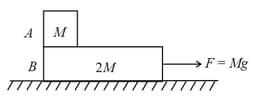
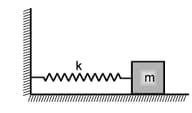
A block of mass is attached to one end of a massless spring of spring constant . The other end of the spring is fixed to a wall. The block can move on a horizontal rough surface. The coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is . The block is released when the spring has a compression of then choose the incorrect option(s):
If the kinetic energy of a particle continuously increases with time then?
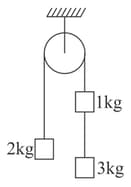
In the following arrangement the pulley is assumed to be light and the string inextensible. The acceleration of the system can be determined by considering the conservation of a certain physical quantity. The physical quantity conserved and the acceleration, respectively, are
A particle free to move along the -axis has potential energy given by, for , where is a positive constant of appropriate dimensions. Then, select the incorrect options.
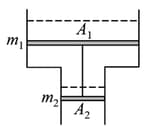
Consider a vertical tube open at both ends. The tube consists of two parts, each of different cross-sections and each part having a piston which can move smoothly in respective tubes. The two pistons are joined together by an inextensible wire. The combined mass of the two pistons is and area of cross-section of the upper piston is greater than that of the lower piston. The amount of gas enclosed by the pistons is one mole. When the gas is heated slowly, the pistons moves by as shown in figure. The rise in temperature of the gas is in the form , where is universal gas constant. Use, and outside pressure. Fill value of .