Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 5: Exercise 5
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 5: Exercise 5
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 10: Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 5: Exercise 5 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Alpha Question Bank for Medical: Chemistry solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 5: Exercise 5 with Hints & Solutions
The specific rate constant of a first order reaction depends upon the,
The reaction, , occurs by the following mechanism
very rapid equilibrium.
slow.
very fast.
What is the rate law for this reaction?
The rate constant is numerically the same for three reactions of first, second and third-order, respectively. Which of the following is correct?
Two substances and are taken in such a way that initially, The time after which both the concentrations will be equal is: (Assume that the reaction is first order)
If for a reaction in which converts to the reaction carried out at constant results into the following graph.
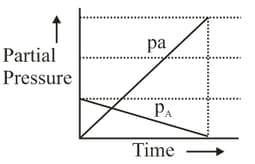
The reaction of hydrogen and iodine monochloride is given as:
The reaction is of a first-order, with respect to and following mechanisms were proposed.
Mechanism
Mechanism
slow
fast
Which of the above mechanism(s) can be consistent with the given information about the reaction?
The bromination of acetone that occurs in acid solution is represented by the equation
These kinetic data were obtained for given reaction concentrations.
Initial concentrations,
Initial Rate, disappearance of
Based on these data, the rate of reaction is :
The reaction is first order in with rate constant . What is the value of rate of reaction when ?
