Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Atomic Physics, Exercise 2: Exercise-2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Atomic Physics, Exercise 2: Exercise-2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 33: Atomic Physics, Exercise 2: Exercise-2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Atomic Physics, Exercise 2: Exercise-2 with Hints & Solutions
In a hydrogen atom, the electron is in excited state. It may come down to second excited state by emitting ten different wavelengths. What is the value of ?
An electron in hydrogen atom after absorbing energy photons can jump between energy states and Then it may return to ground state after emitting six different wavelengths in emission spectrum. The energy of emitted photons is either equal to, less than or greater than the absorbed photons. Then and are :-
The electron in a hydrogen atom makes transition from $M$ shell to $L$. The ratio of magnitudes of initial to final centripetal acceleration of the electron is :-
Monochromatic radiation of wavelength is incident on a hydrogen sample containing in ground state. Hydrogen atoms absorb the light and subsequently emit radiations of ten different wavelengths. The value of is
In an atom, two electrons move around the nucleus in circular orbits of radii and The ratio of the time taken by them to complete one revolution is (neg.'ect electric interaction) :-
The magnitude of angular momentum, orbit radius and frequency of revolution of electron in hydrogen atom corresponding to quantum number are and respectively. Then according to Bohr's theory of hydrogen atom
In a Coolidge tube experiment, the minimum wavelength of the continuous -ray spectrum is equal to then
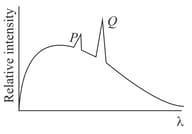
In the characteristic -ray spectra given in the figure of some atom superimposed on continuous -ray spectra