Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Heat Transfer, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Heat Transfer, Exercise 3: Exercise-3
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 16: Heat Transfer, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Engineering: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Heat Transfer, Exercise 3: Exercise-3 with Hints & Solutions
Two metal cubes with -edge of copper and aluminium are arranged as shown in figure. Find
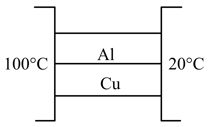
The total thermal current from one reservoir to the other. The thermal conductivity of copper is and that of aluminium is .
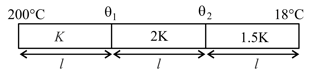
Calculate and in shown situation.
An electric heater is used in a room of total wall area to maintain a temperature of inside it, when the outside temperature is . The walls have three different layers of materials. The innermost layer is of wood of thickness , the middle layer is of cement of thickness and the outermost layer is of brick of thickness . The power of electric heater (in ) is . Write the value of to the nearest integer. Assume that there is no heat loss through the floor and the ceiling. The thermal conductivities of wood, cement and brick are and , respectively.
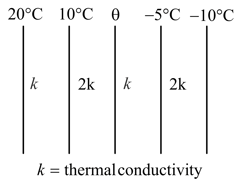
The figure shows the face and interface temperature of a composite slab consisting of four layers of two materials having identical thickness. Under steady state condition, find the value of temperature in.
A lagged stick of cross-section area length are and length is initially at a temperature of . It is then kept between resevoirs of temperature and Specific heat capacity is and linear mass density is .
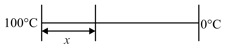
(i) If temperature gradient along the rod in steady state is then find the value of .
(ii) If total heat absorbed by the rod to reach steady state is then find the value of .
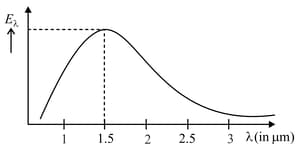
Calculate the temperature of the black body from given graph.