Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 3: BEGINNER'S BOX - 3
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 3: BEGINNER'S BOX - 3
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 9: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 3: BEGINNER'S BOX - 3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Beta Question Bank for Medical: Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions, Exercise 3: BEGINNER'S BOX - 3 with Hints & Solutions
A particle of mass moving with velocity strikes a stationary particle of mass and sticks to it. Find the speed of the system.
Two putty balls of equal masses moving in mutually perpendicular directions with equal speed, stick together after the collision. If the balls were initially moving with a velocity of each, find the velocity of the combined mass after the collision.
A body of mass having velocity collides with a body of mass moving with a velocity of in the opposite direction. After the collision, both bodies stick together and move with a common velocity. Find the velocity in .
A ball is thrown vertically upward from the ground with speed . It collides with the ground after returning. Find the total distance travelled and time taken during its bouncing.
A particle falls from a height ‘’ upon a fixed horizontal plane and rebounds. If is the coefficient of restitution. Find the total distance travelled before rebounding has stopped.
Two balls of equal masses undergo a head-on collision with speeds 6 m/s moving in opposite direction. If the coefficient of restitution is , find the speed of each ball after impact in m/s.
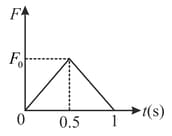
A body of mass moving with velocity makes an elastic one-dimensional collision with an identical stationary body. They are in contact for a brief period . Their force of interaction increases from zero to linearly in and decreases linearly to zero in a further as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude of force in newtons:
A particle of mass moving with a velocity collides head-on with another particle of mass moving with a velocity . After the collision, the first particle has speed of in negative direction. Find the:
(a) velocity of the centre of mass after the collision.
(b) velocity of the second particle after the collision.
(c) coefficient of restitution.
