M L Aggarwal Solutions for Chapter: Quadrilaterals, Exercise 2: Exercise 8.2
M L Aggarwal Mathematics Solutions for Exercise - M L Aggarwal Solutions for Chapter: Quadrilaterals, Exercise 2: Exercise 8.2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 8: Quadrilaterals, Exercise 2: Exercise 8.2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. CBSE Syllabus Standard Mathematics for Class IX solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from M L Aggarwal Solutions for Chapter: Quadrilaterals, Exercise 2: Exercise 8.2 with Hints & Solutions
In a quadrilateral, the angles are in a ratio . If the difference between the greatest and the smallest angle is , find .
In the given quadrilateral, and the bisectors of and meet at . If , find .
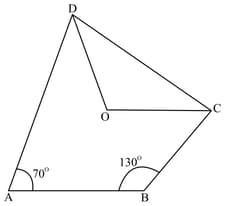
In the given figure, is a parallelogram. If and . If , find .
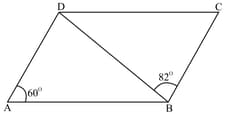
In a trapezium . If , find .

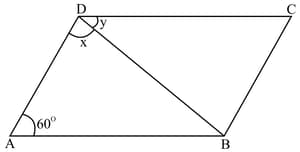
In the given figure, is a parallelogram. If and , then find the values of and .
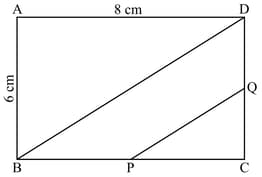
If and . and are mid-points of and , respectively. If the length of is , find in decimal number.
In the given figure, is a rectangle in which and . and are mid-points of the sides and , respectively. If the length of , find .
In a parallelogram , if and , then find the values of and .
