Richard Harwood and Ian Lodge Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Reactions, Exercise 3: Exercise 4.3
Richard Harwood Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Richard Harwood and Ian Lodge Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Reactions, Exercise 3: Exercise 4.3
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 4: Chemical Reactions, Exercise 3: Exercise 4.3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Workbook 4th Edition solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Richard Harwood and Ian Lodge Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Reactions, Exercise 3: Exercise 4.3 with Hints & Solutions
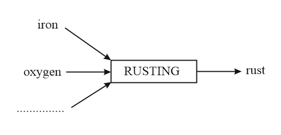
Complete the diagram shown that substances are used and what is produced in burning, respiration and rusting.
Complete the following passage by using the words listed below:
anode, electrodes, current, molten, electrolyte, solution, cathode, positive, hydrogen, molecules, lose, oxygen.
During electrolysis, ionic compounds are decomposed by the passage of an electric current. For this to happen, the compound must be either _____ or _____ in _____. Electrolysis can occur when an electric _____ passes through a molten _____. The two rods dipping into the electrolyte are called the _____. In this situation, metals are deposited at the _____ and non-metals arc formed at the _____.
When the ionic compound is dissolved in water, the electrolysis can be more complex. Generally, during electrolysis _____ ions move towards the _____ and negative ions move towards the _____. At the negative electrode (cathode) the metal or _____ ions gain electrons and form metal atoms or hydrogen _____. At the positive electrode (anode) certain non-metal ions _____ electrons and ______ or chlorine is produced.
Complete the passage by using the words listed below:
hydrogen, hydroxide, lower, copper, sodium, molten, cryolite, purifying, positive, concentrated.
There are several important industrial applications of electrolysis, the most important economically being the electrolysis of ______ aluminium oxide to produce aluminium. The aluminium oxide is mixed with molten _____ to _____ the melting point of the electrolyte.
An ______ aqueous solution of sodium chloride contains _____ chloride, hydrogen and _____ ions. When this solution is electrolysed ______ rather than sodium is discharged at the negative electrode. The solution remaining is sodium hydroxide.
When a solution of copper(II) sulphate is electrolysed using ______ electrodes, an unusual thing happens and the copper atoms of the ______ electrode (anode) go into solution as copper ions. At the cathode, the copper ions turn into copper atoms, and the metal is deposited on this electrode. This can be used as a method of refining or _____ impure copper.
