Mary Jones and Geoff Jones Solutions for Chapter: Homeostasis, Exercise 2: End-of-chapter questions
Mary Jones Biology Solutions for Exercise - Mary Jones and Geoff Jones Solutions for Chapter: Homeostasis, Exercise 2: End-of-chapter questions
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 14: Homeostasis, Exercise 2: End-of-chapter questions with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Cambridge IGCSE® Biology Coursebook Third Edition solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Mary Jones and Geoff Jones Solutions for Chapter: Homeostasis, Exercise 2: End-of-chapter questions with Hints & Solutions
The following sentence contains incorrect information. Identify what is wrong and write the correct sentence.
The fatty layer under the skin stops cold air getting into the body.
The following sentence contains incorrect information. Identify what is wrong and write the correct sentence.
When we are too hot, our sweat glands secrete a cold liquid that cools us down.
The following sentence contains incorrect information. Identify what is wrong and write the correct sentence.
When you are too hot, your blood capillaries move closer to the skin surface.
The following sentence contains incorrect information. Identify what is wrong and write the correct sentence.
Insulin is an enzyme that changes glucose to glycogen.
When a person is submerged in cold water, their body temperature can drop very quickly.
This is because heat is transferred quickly, by conduction, from the warm body into the cold water. An experiment was carried out to see if it is better to stay still if you fall into cold water or try to swim.
- Two men sat for 30 minutes, in the air at a temperature of 150C.
- They then got into the swimming pool, where the water was also at a temperature of 150C,
- Person A swam for the next 30 minutes. Person B lay still in the water.
The body temperature of both men was measured at 10-minute intervals throughout the experiment. The results are shown in the graph.
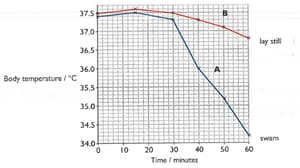
State the body temperature of each man at the start of the experiment.
When a person is submerged in cold water, their body temperature can drop very quickly.
This is because heat is transferred quickly, by conduction, from the warm body into the cold water. An experiment was carried out to see if it is better to stay still if you fall into cold water or try to swim.
- Two men sat for 30 minutes, in the air at a temperature of 15oC.
- They then got into the swimming pool, where the water was also at a temperature of 15oc,
- Person A swam for the next 30 minutes. Person B lay still in the water.
The body temperature of both men was measured at 10-minute intervals throughout the experiment. The results are shown in the graph.
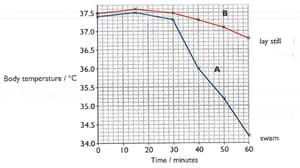
Explain why their body temperature remained roughly constant for the first 30 minutes of the experiment.
When a person is submerged in cold water, their body temperature can drop very quickly.
This is because heat is transferred quickly, by conduction, from the warm body into the cold water. An experiment was carried out to see if it is better to stay still if you fall into cold water or try to swim.
- Two men sat for 30 minutes, in the air at a temperature of 150C.
- They then got into the swimming pool, where the water was also at a temperature of 150c,
- Person A swam for the next 30 minutes. Person B lay still in the water.
The body temperature of both men was measured at 10-minute intervals throughout the experiment. The results are shown in the graph.
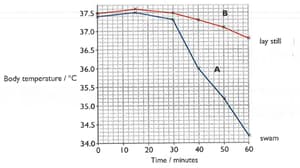
Explain why their body temperature of both the men dropped between 30 and 60 minutes?
When a person is submerged in cold water, their body temperature can drop very quickly.
This is because heat is transferred quickly, by conduction, from the warm body into the cold water. An experiment was carried out to see if it is better to stay still if you fall into cold water or try to swim.
- Two men sat for 30 minutes, in the air at a temperature of 150C.
- They then got into the swimming pool, where the water was also at a temperature of 150c,
- Person A swam for the next 30 minutes. Person B lay still in the water.
The body temperature of both men was measured at 10-minute intervals throughout the experiment. The results are shown in the graph.
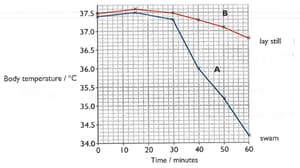
Suggest why person A's temperature dropped faster than the person B's temperature during this time period.
