D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: Projectile Motion, Exercise 1: Excercise 1
D. C. Pandey Physics Solutions for Exercise - D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: Projectile Motion, Exercise 1: Excercise 1
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 4: Projectile Motion, Exercise 1: Excercise 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Complete Study Pack for Engineering Entrances Objective Physics Vol 1 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: Projectile Motion, Exercise 1: Excercise 1 with Hints & Solutions
The trajectory of a projectile near the surface of the earth is given as . If it were launched at an angle with speed , then (Take, )
In a three-dimensional system, the position coordinates of a particle (in motion) are given below . The velocity of the particle will be
A body is projected at with a velocity at an angle of with the horizontal. The radius of curvature of its trajectory at is . Neglecting air resistance and taking acceleration due to gravity , the value of is
A projectile is thrown in the upward direction making an angle of with the horizontal with a velocity of Then the time after which its velocity makes an angle with the horizontal is (Acceleration due to gravity, )
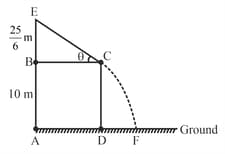
A rough inclined plane of height is kept on a rectangular wooden block of height , as shown in the figure. A small block is allowed to slide down from the top of the inclined plane. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the inclined plane is and the angle of inclination of the inclined plane is . If the small block finally reaches the ground at a point , then will be (Acceleration due to gravity, )
Two boys conducted experiments on the projectile motion with a stopwatch and noted some readings. As one boy throws a stone in the air at the same angle as the horizontal, the other boy observes that after , the stone is moving at an angle to the horizontal and after another, it is traveling horizontally. The magnitude of the initial velocity of the stone is (Acceleration due to gravity, )
A ball is projected vertically up from the ground. The boy standing at the window of the first floor of a nearby building observes that the time interval between the ball crossing him while going up and the ball crossing him while going down is . Another boy standing on the second floor notices that time interval between the ball passing him twice, during up motion and down motion is . Calculate the difference between the vertical positions of boy and boy (Assume, acceleration due to gravity, )
Two particles are simultaneously projected in the horizontal direction from a point at a certain height. The initial velocities of the particles are oppositely directed to each other and have magnitude each. The separation between the particles at a time when their position vectors (drawn from the point ) are mutually perpendicular, is
