D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: The First Law of Thermodynamics, Exercise 2: Excercise 2
D. C. Pandey Physics Solutions for Exercise - D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: The First Law of Thermodynamics, Exercise 2: Excercise 2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 15: The First Law of Thermodynamics, Exercise 2: Excercise 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Complete Study Pack for Engineering Entrances Objective Physics Vol 1 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from D. C. Pandey Solutions for Chapter: The First Law of Thermodynamics, Exercise 2: Excercise 2 with Hints & Solutions
In a process, temperature and volume of one mole of an ideal mono-atomic gas are varied according to the relation, , where is a constant. In this process, the temperature of the gas is increased by . The amount of heat absorbed by gas is (where is gas constant),
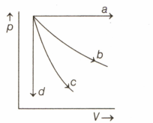
The given diagram shows four processes, i.e., isochoric, isobaric, isothermal and adiabatic. The correct assignment of the processes in the same order is given by,
An ideal mono-atomic gas at expands adiabatically to twice its volume. The final temperature of gas is,
One mole of Nitrogen gas being initially at a temperature, is adiabatically compressed to increase its pressure times. The final gas temperature after compression is (assume Nitrogen gas molecules as rigid and diatomic and ),
If the speed of sound in a mixture of moles of Helium and moles of Hydrogen at temperature is , then the value of is (Take, )
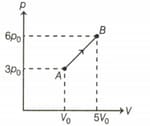
One mole of a monatomic ideal gas undergoes the process in the given diagram. Specific heat capacity in the process is
If is the coefficient of performance of a refrigerator and is heat released to the hot reservoir, then the heat extracted from the cold reservoir is,
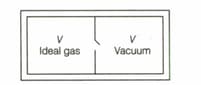
Consider the given diagram. An ideal gas is contained in a chamber (left) of volume and is at an absolute temperature . It is allowed to rush freely into the right chamber of volume which is initially vacuum. The whole system is thermally isolated. What will be the final temperature of the equilibrium has been attained?