Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Equilibrium, Exercise 1: JEE Advanced Paper 2 - 2016
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Equilibrium, Exercise 1: JEE Advanced Paper 2 - 2016
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 5: Equilibrium, Exercise 1: JEE Advanced Paper 2 - 2016 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. EMBIBE CHAPTER WISE PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS FOR CHEMISTRY solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Equilibrium, Exercise 1: JEE Advanced Paper 2 - 2016 with Hints & Solutions
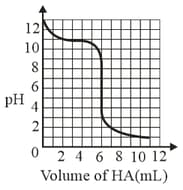
A solution of weak base is titrated with of a strong acid . The variation of of the solution with the volume of added is shown in the figure below. What is the of the base? The neutralisation reaction is given by .
An acidified solution of is saturated with . What is the minimum molar concentration of required to prevent the precipitation of ? Use and overall dissociation constant of
Consider an electrochemical cell: . The value of for the cell reaction is twice that of at If the emf of the cell is zero, the magnitude of of the cell reaction per mole of formed at is ____ . (Give answer after rounding off to the nearest integer value.)
(Given: R and are enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs energy, respectively.)
When 100 mL of 1.0 M HCl was mixed with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH in an insulated beaker at constant pressure, a temperature increase of was measured for the beaker and its contents (Expt.1). Because the enthalpy of neutralization of a strong acid with a strong base is a constant , this experiment could be used to measure the calorimeter constant. In a second experiment (Expt. 2), 100 mL of 2.0 M acetic acid was mixed with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH (under identical conditions to Expt. 1) where a temperature rise of was measured. (Consider heat capacity of all solutions as and density of all solutions as )
The pH of the solution after Expt. 2 is
Consider the reaction at . At the time , the temperature of the system was increased to and the system was allowed to reach equilibrium. Throughout this experiment the partial pressure of was maintained at bar. Given below is the plot of the partial pressure of with time. What is the ratio of the standard Gibbs energy of the reaction at to that at ?
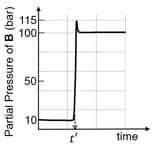
Give your answer by multiplying with 100 and rounding off to nearest integer.
For the following reaction, the equilibrium constant at is
When equal volumes of and solutions are mixed, the equilibrium concentration of is found to be The value of is __________ (Answer should be given to the nearest integer value).
The solubility of a salt of weak acid . The value of is ____(Nearest integer). (Given that the value of solubility product of , and the value of ionisation constant of )
The % yield of ammonia as a function of time in the reaction
at is given below.
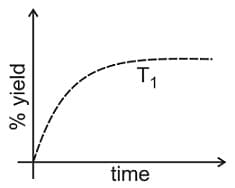
If this reaction is conducted at with , the % yield of ammonia as a function of time is represented by:
