Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 1: Level 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 1: Level 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 1: Level 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course JEE Main solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Work, Energy and Power, Exercise 1: Level 1 with Hints & Solutions
A block starts moving up an inclined plane of inclination with an initial velocity of . It comes back to its initial position with velocity . The value of the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the inclined plane is close to The nearest integer to is _____.
The displacement of an object of mass is given by the relation , where is time in seconds. If the work done by the net force on the object in is , where and are smallest integer values, then what is the value of ?
A point-like mass moves horizontally between two walls on a frictionless surfaces with initial kinetic energy With every collision with the walls, the mass loses of its kinetic energy to thermal energy. How many collisions with the walls are necessary before the speed of the mass is reduced by a factor of (means it becomes th of initial speed) ?
The potential energy of a diatomic molecule is a function dependent on (interatomic distance) as , where, and are positive constants. The equilibrium distance between two atoms is , where
A car of mass is driven with acceleration along a straight level road against a constant external resistive force When the velocity of the car is the rate at which the engine of the car is doing work will be
A small sphere of mass is moving with a velocity . It hits a fixed smooth wall and rebound with velocity . If the coefficient of restitution between the sphere and the wall is , then find the value of .
A ball with a speed of collides with another identical ball at rest. After thecollision, the direction of each ball makes an angle of with the original direction. The ratio of velocities of the balls after collision is where is
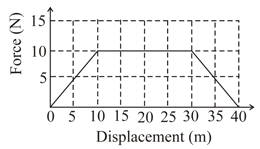
Adjacent figure shows the force-displacement graph of a moving body, the work done in displacing body from to is equal to