Priyanka B Solutions for Chapter: Forces and Laws of Motion, Exercise 5: NCERT Exemplar Problems
Priyanka B Physics Solutions for Exercise - Priyanka B Solutions for Chapter: Forces and Laws of Motion, Exercise 5: NCERT Exemplar Problems
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 2: Forces and Laws of Motion, Exercise 5: NCERT Exemplar Problems with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Essentials of PHYSICS Class IX solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Priyanka B Solutions for Chapter: Forces and Laws of Motion, Exercise 5: NCERT Exemplar Problems with Hints & Solutions
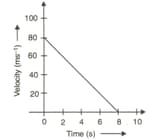
Velocity versus time graph of a ball of mass rolling on a concrete floor is shown in figure. Calculate the acceleration and frictional force of the floor on the ball.
A truck of mass is moved under a force . If the truck is then loaded with an object equal to the mass of the truck and the driving force is halved, then how does the acceleration change ?
Two friends on a roller skates are standing apart facing each other. One of them throws a ball of towards the other, who catches it. How will this activity effect the position of the two ? Explain your answer.
Water sprinkler used for grass lawns begins to rotate as soon as the water is supplied. Explain the principle on which it works.
Using second law of motion, derive the relation between force and acceleration. A bullet of strikes a sand-bag a speed of and gets embedded after travelling . Calculate
The resistance force exerted by the sand on the bullet.
A bullet of strikes a sand-bag a speed of and gets embedded after travelling .Calculate
(ii) The time taken by bullet to come to rest.
Derive the unit of force using the second law of motion. A force of produces an acceleration of on a mass and an acceleration of on a mass . What acceleration would the same force provide if both the masses tied together ?
What is Momentum? Write its S.I unit. Interpret force in terms of momentum.
Represent the following graphically :
(a) momentum versus velocity when mass is fixed.
(b) momentum versus mass when velocity is constant.
