G L Mittal and TARUN MITTAL Solutions for Chapter: Motion in One and Two Dimensions, Exercise 3: FOR DIFFERENT COMPETITIVE EXAMINATIONS
G L Mittal Physics Solutions for Exercise - G L Mittal and TARUN MITTAL Solutions for Chapter: Motion in One and Two Dimensions, Exercise 3: FOR DIFFERENT COMPETITIVE EXAMINATIONS
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 8: Motion in One and Two Dimensions, Exercise 3: FOR DIFFERENT COMPETITIVE EXAMINATIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. ISC Physics Class XI Part 1 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from G L Mittal and TARUN MITTAL Solutions for Chapter: Motion in One and Two Dimensions, Exercise 3: FOR DIFFERENT COMPETITIVE EXAMINATIONS with Hints & Solutions
An object, moving with a speed of , is decelerated at a rate given by, where is the instantaneous speed. The time taken by the object, to come to rest, would be:
A particle is moving with velocity , where is a constant. The general equation for its path is:
A projectile is fired from the surface of the earth with a velocity of and angle with the horizontal. Another projectile fired from another planet with a velocity of at the same angle follows a trajectory which is identical with the trajectory of the projectile fired from the earth. The value of the acceleration due to gravity on the planet is (in )
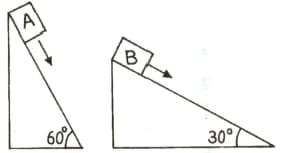
Two fixed frictionless inclined planes making an angle and with the vertical are shown in the figure. Two blocks and are placed on the two planes. What is the relative vertical acceleration of with respect to .
A particle of mass is projected from the ground with an initial speed at an angle with the horizontal. At the highest point of its trajectory, it makes a completely inelastic collision with another identical particle, which was thrown vertically upward from the ground with the same initial speed . The angle that the composite system makes with the horizontal immediately after the collision is:
A particle of mass is projected with velocity making an angle of with the horizontal. When the particle lands on the level ground the magnitude of the change in its momentum will be
A particle is projected at to the horizontal with a kinetic energy . The kinetic energy at the highest point is
A projectile is given an initial velocity of , when is along the ground and is along the vertical. If , the equation of its trajectory is:
