Natasha Awada, Paul La Rondie, Laurie Buchanan and, Jill Stevens Solutions for Chapter: Representing Relationships: Introducing Functions, Exercise 12: Exercise 2B
Natasha Awada Mathematics Solutions for Exercise - Natasha Awada, Paul La Rondie, Laurie Buchanan and, Jill Stevens Solutions for Chapter: Representing Relationships: Introducing Functions, Exercise 12: Exercise 2B
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 2: Representing Relationships: Introducing Functions, Exercise 12: Exercise 2B with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Mathematics : Analysis and Approaches Standard Level Course Companion solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Natasha Awada, Paul La Rondie, Laurie Buchanan and, Jill Stevens Solutions for Chapter: Representing Relationships: Introducing Functions, Exercise 12: Exercise 2B with Hints & Solutions
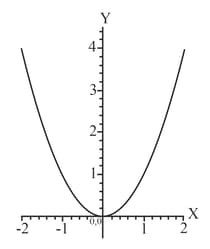
Calculate for the graph below.
To convert a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit, we use the formula: . Use the formula to calculate the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit at which water boils.
To convert a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit, we use the formula: . The average body temperature of the dog is . Convert this to degrees Fahrenheit.
Cookies are generally baked at . Convert this to degrees Fahrenheit (correct up to two decimal places). To convert a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit, we use the formula: .
A British telecommunications company offers the following roaming data package to its customers: a flat fee of plus per gigabyte of data. Express the total cost, , as a function of the number of gigabytes of data .
A British telecommunications company offers the following roaming data package to its customers: a flat fee of plus per gigabyte of data. What values of do not make sense in this context?
A British telecommunications company offers the following roaming data package to its customers: a flat fee of plus per gigabyte of data. State the notation that could be used to find the roaming cost for a trip where gb of data is used? Calculate this value.
A British telecommunications company offers the following roaming data package to its customers: a flat fee of plus per gigabyte of data. State the notation that could be used to find the number of gigabytes of data one can use for a total bill of . Calculate this value.
