Ramendra C Mukerjee Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Equilibrium, Exercise 1: PROBLEMS
Ramendra C Mukerjee Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Ramendra C Mukerjee Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Equilibrium, Exercise 1: PROBLEMS
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 15: Chemical Equilibrium, Exercise 1: PROBLEMS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Modern Approach to Chemical Calculations solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Ramendra C Mukerjee Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Equilibrium, Exercise 1: PROBLEMS with Hints & Solutions
is introduced into three identical bulbs at . Each bulb is opened at different time intervals and analysed for by titrating with hypo solution.
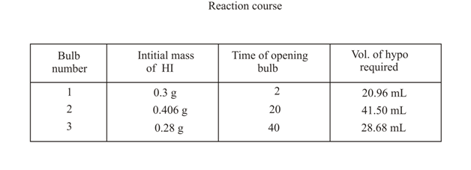
Calculate for at .
Hint: of in .
A flask contains in equilibrium with its decomposition products. For this reaction, . How is the mass of in the flask affected by the following disturbances?
is added
A flask contains in equilibrium with its decomposition products. For this reaction, . How is the mass of in the flask affected by each of the following disturbances? ( is added with no appreciable change in volume)
A flask contains in equilibrium with its decomposition products. For this reaction, . How is the mass of in the flask affected by the following disturbances?
A large amount of is added decreasing the volume available to the gases.
Chlorine molecules are dissociated at at a pressure of of the pressure is due to ). In , calculate and .
Show that, .
Calculate the equilibrium ratio of to if each of and were allowed to come to equilibrium at .
.
Calculate (in kJ) for the reaction for which and .
