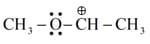NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques, Exercise 1: Matching Type
Author:NCERT
NCERT Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques, Exercise 1: Matching Type
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 12: Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques, Exercise 1: Matching Type with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. NCERT Exemplar Chemistry - Class 11 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques, Exercise 1: Matching Type with Hints & Solutions
MEDIUM
11th CBSE
IMPORTANT
Match the type of mixture of compounds in Column I with the technique of separation/purification given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Two solids which have different solubilities in a solvent and which do not undergo reaction when dissolved in it. | (a) Steam distillation |
| (ii) Liquid that decomposes at its boiling point |
(b) Fractional distillation |
| (iii) Steam volatile liquid |
(c) Simple distillation |
| (iv) Two liquids which have boiling points close to each other |
(d) Distillation under reduced pressure |
| (v) Two liquids with large difference in boiling points. | (e) Crystallization |
HARD
11th CBSE
IMPORTANT
Match the terms mentioned in Column I with the terms in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Carbocation | (a) | Cyclohexane and -hexene |
| (ii) | Nucleophile | (b) | Conjugation of electrons of bond with empty -orbital present at adjacent positively charged carbon. |
| (iii) | Hyperconjugation | (c) | hybridised carbon with the empty orbital |
| (iv) | Isomers | (d) | Ethyne |
| (v) | hybridisation | (e) | Species that can revive a pair of electrons |
| (vi) | Electrophile | (f) | Species that can supply a pair of electrons |
MEDIUM
11th CBSE
IMPORTANT
Match Column I with Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Dumas method | (a) | |
| (ii) | Kjeldahl's method | (b) | Silica gel |
| (iii) | Carius method | (c) | Nitrogen gas |
| (iv) | Chromatography | (d) | Free radicals |
| (v) | Homolysis | (e) | Ammonium sulphate |
MEDIUM
11th CBSE
IMPORTANT
Match the intermediates given in Column I with their probable structure in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Free radical | (a) | Trigonal planar |
| (ii) | Carbocation | (b) | Pyramidal |
| (iii) | Carbanion | (c) | Linear |
HARD
11th CBSE
IMPORTANT
Match the ions given in Column I with their nature-given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) |
|
(a) | Stable due to resonance |
| (ii) | (b) | Destabilised due to inductive effect | |
| (iii) | 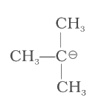 |
(c) | Stabilised by hyperconjugation |
| (iv) | (d) | A secondary carbocation |