NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Magnetism and Matter, Exercise 3: SA
NCERT Physics Solutions for Exercise - NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Magnetism and Matter, Exercise 3: SA
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter, Exercise 3: SA with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. NCERT Exemplar Physics - Class 12 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Magnetism and Matter, Exercise 3: SA with Hints & Solutions
Verify the Gauss’s law for magnetic field of a point dipole of dipole moment at the origin for the surface which is a sphere of radius .
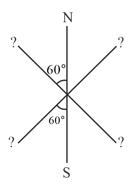
Three identical bar magnets are rivetted together at centre in the same plane as shown in figure. This system is placed at rest in a slowly varying magnetic field. It is found that the system of magnets does not show any motion. The north-south poles of one magnet is shown in the figure. Determine the poles of the remaining two.
Suppose we want to verity the analogy between electrostatic and magneto static by an explicit experiment. Consider the motion of electric dipole in an electrostatic field and magnetic dipole m in a magnetic field . Write down a set of conditions on so that the two motions are verified to be identical. (Assume identical initial conditions.)
A bar magnet of magnetic moment m and moment of inertia (about centre, perpendicular to length) is cut into two equal pieces, perpendicular to length. Let be the period of oscillations of the original magnet about an axis through the mid point, perpendicular to length, in a magnetic field . What would be the similar period for each piece?
Use the Ampere’s law for and continuity of lines of , to conclude that inside a bar magnet, lines of run from the pole to pole, while lines of must run from the pole to pole.
