NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 3: SA
NCERT Physics Solutions for Exercise - NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 3: SA
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 4: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 3: SA with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. NCERT Exemplar Physics - Class 12 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Moving Charges and Magnetism, Exercise 3: SA with Hints & Solutions
A current carrying loop consists of identical quarter circles of radius , lying in the positive quadrants of the and planes with their centres at the origin, joined together. Find the direction and magnitude of at the origin.
A charged particle of charge and mass is moving in an electric field and magnetic field . Construct dimensionless quantities and quantities of dimension .
An electron enters with a velocity into a cubical region (faces parallel to coordinate planes) in which there are uniform electric and magnetic fields. The orbit of the electron is found to spiral down inside the cube in plane parallel to the x-y plane. Suggest a configuration of fields and that can lead to it.
Do magnetic forces obey Newton’s third law. Verify for two current elements located at the origin and located at . Both carry current .
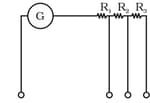
A multirange voltmeter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit, as shown in figure. We want to construct a voltmeter that can measure , and using a galvanometer of resistance and that produces maximum deflection for current of . Find , and that have to be used.
A long straight wire carrying current of rests on a table as shown in figure. Another wire of length , mass carries the same current but in the opposite direction. The wire is free to slide up and down. To what height will rise?