B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Superposition and Standing Waves, Exercise 2: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Superposition and Standing Waves, Exercise 2: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 7: Superposition and Standing Waves, Exercise 2: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS FOR JOINT ENTRANCE EXAMINATION WAVES AND THERMODYNAMICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Superposition and Standing Waves, Exercise 2: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE with Hints & Solutions
A tube closed at one end has a vibrating diaphragm at the other end, which may be assumed to be a displacement node. It is found that when the frequency of the diaphragm is a stationary wave pattern is set up in which the distance between adjacent nodes is When the frequency is gradually reduced, the stationary wave pattern disappears but another stationary wave pattern reappears at a frequency of Calculate the distance between the diaphragm and the closed-end,
A tube closed at one end has a vibrating diaphragm at the other end, which may be assumed to be a displacement node. It is found that when the frequency of the diaphragm is a stationary wave pattern is set up in which the distance between adjacent nodes is When the frequency is gradually reduced, the stationary wave pattern disappears but another stationary wave pattern reappears at a frequency of Calculate the next lower frequencies at which stationary wave patterns will be obtained.
The first overtone of a pipe closed at one of its end is Find the fundamental frequency of this pipe open at both ends.
An organ pipe has two successive harmonics with frequencies and Find these harmonics and the length of the rube. Assume the sound speed
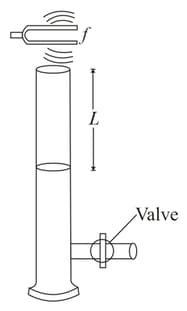
A tuning fork with a frequency of is placed near the top of the tube shown in figure. The water level is lowered so that the length slowly increases from an initial value of Determine the next two values of that correspond to resonant modes. Assume the sound speed
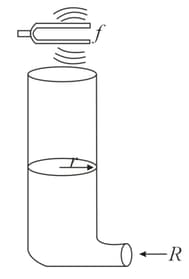
In the given figure, water is being pumped into a tall, vertical cylinder at a volume flow rate The radius of the cylinder is and at the open top of the cylinder a tuning fork is vibrating with a frequency As the water rises, what time interval elapses between successive resonances?
A student is listening to the sounds from an air column that is long. He doesn't know if the column is open at both ends or open at only one end. He hears resonance from the air column at frequencies and Justify, why the above given situation is impossible.
A hard metallic rod fixed at one of its ends is fitted with a vibrator at the other end. The vibrator is electrically driven and sets up a longitudinal wave that moves along the rod. The waves get reflected at the fixed end The reflected waves superimpose with the waves sent by the vibrator. For the resonance to occur, a strong longitudinal standing wave is generated in the rod. Find the frequency of the vibrator if the rod resonates with its overtone. [Put
