B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 3: Exercises
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 3: Exercises
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 4: Thermodynamics, Exercise 3: Exercises with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS FOR JOINT ENTRANCE EXAMINATION WAVES AND THERMODYNAMICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 3: Exercises with Hints & Solutions
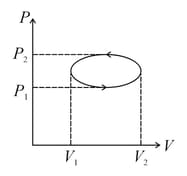
In the given elliptical diagram
Four moles of hydrogen, two moles of helium and one mole of water vapour form an ideal gas mixture. What is. the molar specific heat at constant pressure of mixture ?
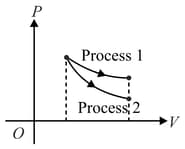
The indicator diagram for two process and carried on an ideal gas is shown in figure. If and be the slopes for process and process respectively, then:-
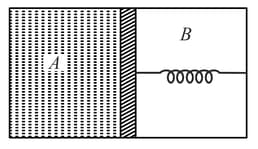
A thermally insulated chamber of volume is divided by a frictionless piston of area into two equal parts and . Part has an ideal gas at pressure and temperature and in part is vacuum. A massless spring of force constant is connected with piston and the wall of the container as shown. Initially spring is unstarched. Gas in chamber is allowed to expand. Let in equilibrium spring is compressed by . Then
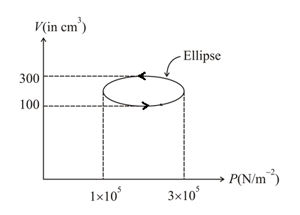
Calculate the heat absorbed by a system in going through the cyclic process shown in the given figure.
(Take )
gas undergoes a change of state during which of heat is supplied to it and it does of work. The system is brought back to its original state through a process during which of heat is rejected by the gas. Find the work done by the gas in the second process in joules.
A sample of an ideal gas is taken through a process . It absorbs of energy during the process which is an isometric process, no heat during and it rejects of heat during isobaric process . It is also given that of work is done on the gas during the process . Internal energy of gas in state is . Find the internal energy of gas in state in joules.
A gas consisting of rigid diatomic molecules was expanded polytropic process so that the rate of collisions of the molecules against the vessel's wall did not change. Find the molar heat capacity of the gas in this process in . (Given: Gas constant )
