B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Kinematics II, Exercise 23: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 5.2
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Kinematics II, Exercise 23: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 5.2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 5: Kinematics II, Exercise 23: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 5.2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS For Joint Entrance Examination JEE (Advanced) Mechanics I solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Kinematics II, Exercise 23: CONCEPT APPLICATION EXERCISE 5.2 with Hints & Solutions
A grasshopper can jump a maximum distance of . It spends negligible time on the ground. How far can it go in ?
A projectile is thrown with an initial velocity of . If the range of a projectile is double the maximum height reached by it. Find the ratio .
A ball is thrown at different angles with the same speed and from the same points and it has the same range in both cases. If and be the heights attained in the two cases, then find the value of .
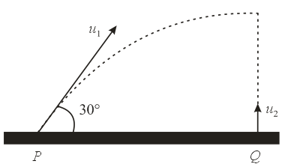
A particle is projected with the velocity at an angle of with the horizontal. Another particle is thrown vertically upwards with velocity from a point vertically below the highest point of the path of . Determine the necessary condition for the two particles to collide at the highest point.
Two seconds after projection, a projectile is travelling in a direction inclined at to horizontal. After one more second, it is travelling horizontally. Find the magnitude and direction of its velocity.
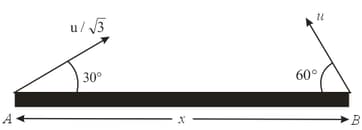
Two particles are separated at a horizontal distance as shown in the figure. They are projected at the same time as shown in the figure with different initial speeds. Find the time after which the horizontal distance between the particles becomes zero.
The horizontal range of a projectile becomes from due to wind in the horizontal direction. Here, is the maximum height reached by the projectile. What constant horizontal acceleration is imparted by the wind.
A boy is running along the positive -axis with . While running he manages to throw a stone in a plane perpendicular to his direction of running with the velocity at an angle with vertical. Find the speed of the stone at the highest point of the trajectory.
